-
×
 PT-141 (Bremelanotide) 10MG
1 × $39.99
PT-141 (Bremelanotide) 10MG
1 × $39.99
MGF (Mechano Growth Factor) 2mg
$32.99
You save
This product is intended as a research chemical only. This designation allows the use of this chemical strictly for in-vitro laboratory testing and experimentation. Human or veterinary use is strictly forbidden. This product is not a drug, food or cosmetic and may not be misbranded, mislabeled or misused as such.
Description


Buy MGF Mechano Growth Factor: Research-Grade Peptides for Laboratory Studies
Research into mechano growth factor is uncovering fascinating mechanisms of tissue repair and cellular regeneration. As scientists delve into the complex pathways of muscle recovery and growth factor signaling, the demand for high quality research compounds has grown. For labs looking to buy mgf mechano growth factor, understanding the molecular properties, research applications and quality considerations is key to successful results.
Mgf mechano growth factor is an alternatively spliced variant of insulin like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), specifically the IGF-1Ec isoform. This synthetic peptide has gained attention in research due to its unique mechanisms different from standard IGF-1 pathways. Unlike regular growth factor compounds, MGF works through specialized cellular activation patterns that researchers have linked to tissue repair and muscle growth in experimental models.
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Amino Sequence | Tyr-Gln-Pro-Pro-Ser-Thr-Asn-Lys-Asn-Thr-Lys-Ser-Gln-Arg-Arg-Lys-Gly-Ser-Thr-Phe-Glu-Glu-Arg-Lys (MGF human variant) |
| Molecular Formula | C₁₂₁H₁₉₉N₄₁O₄₀ |
| Molecular Weight | 2868.19 g/mol |
| Alternative Name | IGF-1 Ec (human variant) |
| Research Purity | > 95% when properly manufactured |
The peptide contains specific amino acid sequences such as thr lys ser gln, ser thr asn lys and other critical domains that contribute to its biological activity profile. Research shows the c terminal peptide domain plays a key role in the molecule’s mechanism compared to standard insulin like growth compounds. The PEG modification increases molecular stability and extends the compound’s half life in experimental systems making it more suitable for lab use.
Lab analysis shows properly synthesized MGF is highly soluble in appropriate solvents and maintains molecular integrity when stored under recommended conditions. The peptide’s molecular structure allows researchers to study its interaction with cellular receptors and signaling pathways in controlled experimental conditions.
Mechanism of Action
Research has shown MGF works through distinct cellular pathways different from standard insulin like growth factor mechanisms. When muscle tissues experience mechanical stress or damage in experimental models, alternative splicing of the IGF-1 gene produces the IGF-1Ec mRNA variant which encodes for mechano growth factor.Research shows MGF’s c terminal peptide domain allows it to work independently of standard IGF-1 receptor pathways. Research suggests this mechanism allows MGF to stimulate muscle satellite stem cells for tissue repair processes while promoting cellular proliferation rather than immediate differentiation, unlike mature IGF-1 which promotes both proliferation and terminal differentiation.
Lab studies have shown synthetic MGF preferentially activates ERK1/2 and ERK5 pathways rather than the conventional Akt pathway associated with IGF I responses. This activation pattern leads to gene expression changes that research suggests favor proliferation and regeneration processes in experimental models.
The compound’s effects on protein synthesis and muscle fibers have been observed in various research settings. Studies have shown MGF treatment can influence myoblast fusion and accelerate muscle fiber formation in lab models. Research suggests this dual action mechanism may enhance tissue repair through rapid satellite cell expansion, priming muscle tissue for effective recovery after experimental overload or damage.
Beyond muscle tissue, research has looked into MGF’s activity in other biological systems. Lab studies have investigated its role in neurogenesis, neuroprotection, cardiac function enhancement and various smooth muscle system responses in experimental models.
Research Studies
Extensive lab research has provided valuable information on MGF’s biological activities across multiple experimental systems. Research findings from various preclinical models have shown the compound’s effects on cellular processes and tissue responses.
Muscle Research Applications: Lab studies have shown MGF increases muscle precursor cell proliferation after mechanical loading in experimental models. Research shows expression increases in response to exercise, stretch or induced damage in lab settings. In aged muscle tissue models, decreased MGF expression has been linked to impaired regenerative capacity, suggesting potential applications in sarcopenia research.
Neuroprotection Studies: Brain ischemia research has shown MGF’s potential neuroprotective properties. In gerbil models of transient brain ischemia, research has shown increased MGF expression in hippocampal neurons that were resistant to ischemic damage. These findings suggest the compound may play a protective role in neural cell survival under experimental stress conditions.
Cardiac Research: Cardiac research has shown promising results in experimental models. Research has shown MGF delivery after induced myocardial infarction in lab animals resulted in reduced mortality rates and improved cardiac function outcomes. Lab studies suggest these effects may involve reparative and anti-apoptotic signaling pathways that support tissue recovery processes.Advanced Delivery Research: Current research is investigating advanced delivery systems, including fluorescently labeled nanoparticles to target MGF peptides to specific tissues. Research is looking at various disease models, some of which are exploring colorectal cancer treatment approaches using advanced targeting technologies.
Additional research has been done on MGF in smooth muscle hyperplasia, tendon repair and bone marrow cell activity in lab models. These diverse applications show the compound’s broad research potential across multiple biological systems.
Storage and Handling
Proper storage and handling is crucial to maintain peptide integrity and get reliable results when working with MGF compounds. Laboratory best practices require specific environmental conditions and handling procedures to preserve the molecule’s biological activity throughout the experiment.
Storage Requirements: Research grade MGF peptides are shipped as lyophilized powder and should be stored at -20°C or below until ready to use. This storage temperature prevents degradation and maintains the compound’s molecular stability for extended periods. Once received, vial contents should be frozen until reconstitution is needed for the experiment.
Post-Reconstitution Handling: Once reconstituted, peptide solutions should be refrigerated at 2-8°C and used within the time frame specified by the manufacturer. Research experience shows that reconstituted solutions can be stable for days to weeks when stored properly, but this can vary depending on the formulation and storage conditions.
Quality Preservation: Laboratory protocols emphasize avoiding repeated freeze-thaw cycles which can accelerate peptide degradation and compromise the results. Research suggests that aliquoting reconstituted solutions into smaller portions can minimize exposure and maintain the compound’s integrity throughout the experiment.
Professional packaging in pharmaceutical grade glass vials and temperature controlled shipping ensures the compounds reach the laboratory in research grade quality. This is especially important for peptides which can be sensitive to temperature fluctuations and environmental conditions during transport.
Why Buy from Loti Labs
Loti Labs specializes in providing research grade peptides that meet the strict standards required for scientific research. When researchers buy mgf mechano growth factor from established suppliers, they get several benefits to support successful experiments and reliable results.
Quality Assurance: Loti Labs has controlled manufacturing environments with quality control protocols designed specifically for research applications. Each batch is tested to ensure peptides meet research grade purity standards of 99% or higher. This level of quality control ensures consistent results across the experiment and reproducible results.Product Variants and Formulations: PEG modified for stability and bioavailability in research models, standard for specific research applications.
Packaging and Preservation: Professional packaging in pharmaceutical grade glass vials to protect peptide integrity during storage and transport. Temperature controlled shipping to maintain the cold chain to prevent heat induced denaturation that can compromise research results. This ensures compounds arrive at the research facility in optimal condition for immediate use or storage.
Documentation and Traceability: Documentation accompanies each product including certificate of analysis that confirms molecular verification and purity standards. This documentation supports research protocols that require compound characterization and provides traceability for research compliance.
Products from Loti Labs are for Research Use Only
All MGF products sold by Loti Labs are Research Use Only (RUO) which defines the intended use and regulatory status. This designation allows the use of these peptides only for in-vitro laboratory testing and experimental investigations under controlled research conditions.
The RUO designation prohibits any human or veterinary application, administration or use as a substance for therapeutic purposes. These compounds are not intended as food, cosmetic products or any consumer applications. Research facilities and academic institutions use RUO compounds specifically for advancing scientific knowledge through controlled experimental investigations.
This regulatory framework allows researchers to access high quality compounds for legitimate scientific purposes while maintaining compliance with regulations governing research substances. Laboratory professionals understand that RUO compounds require appropriate safety protocols, institutional oversight and adherence to research ethics guidelines in all experimental applications.
Research institutions have specific protocols for handling RUO compounds including storage, waste disposal and documentation requirements. These measures support research integrity and compliance throughout the experiment.
Shipping Policy of Loti Labs
Logistics support research timelines and ensure compounds arrive at the laboratory in optimal condition for immediate use. Loti Labs offers same day shipping for orders placed before 1pm EST Monday through Friday so researchers can minimize delays in their experimental schedule.
Orders placed after the daily cutoff or on weekends ship the next business day to maintain consistent delivery schedules for researchers to plan their experimental timelines. Free shipping on all orders over $149 and bulk discounts for 5 or more vials to support cost effective purchasing for larger research projects.Temperature controlled packaging maintains the cold chain for peptide stability during shipping. Professional packaging protocols protect compounds from environmental factors that can compromise research quality so materials arrive ready for immediate use or lab storage.
Guarantee
Research requires confidence in compound integrity and supplier reliability. Loti Labs offers a 30 day satisfaction guarantee on all MGF products. Researchers can return any unopened products for a full refund of the purchase price.
This guarantee reflects the company’s commitment to research excellence and provides assurance that researchers receive only the highest quality peptides for their research. The policy supports research institutions that require reliable supplier relationships and consistent compound quality across multiple orders.
Quality assurance extends beyond the initial purchase to ongoing support for research applications. Laboratory professionals can rely on consistent compound characteristics and performance across different batches to support reproducible results and research outcomes.
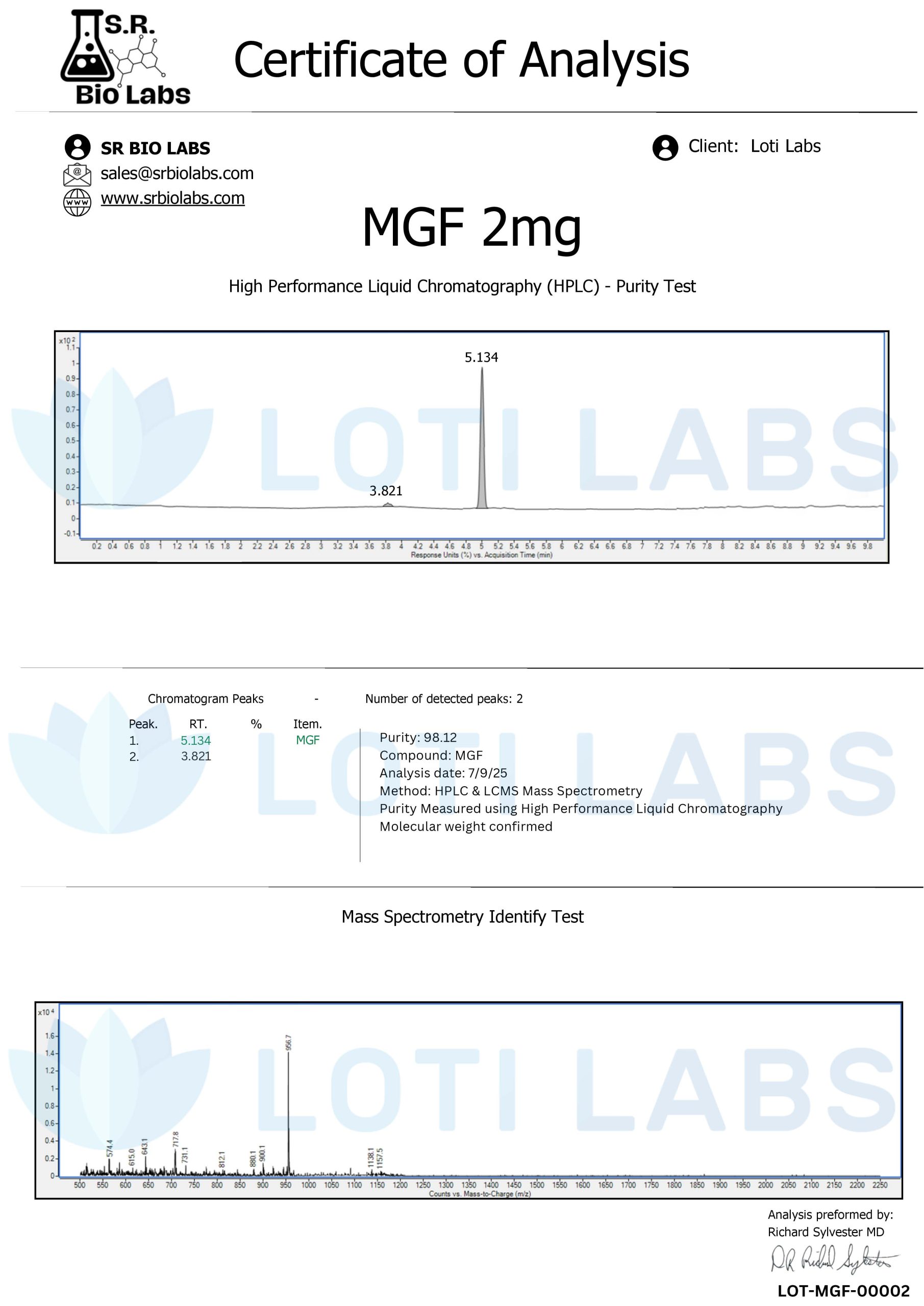
Third Party Testing of Every Batch
Quality control requires independent verification of compound characteristics and purity standards. Every batch of MGF products is tested by a third party using HPLC to verify product purity is above 95% and meets research grade specifications.
Certificates of analysis are available upon request to provide detailed documentation of molecular verification and confirm the absence of contaminants that can compromise research results. This testing protocol ensures researchers receive compounds with consistent molecular characteristics and performance across different experimental applications.
Independent testing provides objective verification of compound quality to support research protocols that require detailed characterization of experimental materials. Laboratory professionals can access analytical data to support their experimental design and ensure compound specifications match their research requirements.
The testing protocol examines molecular integrity, purity levels and presence of impurities that can affect experimental results. This comprehensive approach ensures researchers can proceed with confidence in their experimental design and expect consistent results from their MGF research.
Conclusion
Research into mechano growth factor is revealing complex mechanisms of tissue repair, cellular regeneration and growth factor signaling pathways. As science advances the availability of high quality research compounds becomes more critical to support rigorous research and advance knowledge in this field.
For researchers looking to buy mgf mechano growth factor, consideration of supplier quality standards, regulatory compliance and product specifications will ensure successful research outcomes. The unique molecular characteristics of MGF including its mechanism of alternative splicing of insulin like growth factor pathways make it a valuable tool to investigate tissue repair and cellular responses in controlled lab settings.Research has shown MGF can be applied to various research areas from muscle biology and regeneration to neuroprotection and cardiac research. The compound’s unique mechanism of action distinct from IGF I provides researchers opportunities to explore new therapeutic targets and understand complex biological processes.
Research requires reliable suppliers who understand the strict standards of scientific research. When choosing research compounds consider molecular verification, purity standards, storage protocols and regulatory compliance to ensure successful research outcomes and reproducible results.
As growth factor research continues to evolve access to well characterized, high purity compounds supports the advancement of knowledge and new understanding in tissue biology, regenerative processes and cellular signaling pathways. For laboratory professionals committed to advancing science through rigorous research selecting the right supplier and handling protocols ensures research contributes to the growing body of knowledge in this field.
References
- Peña, J. R., Pinney, J. R., Ayala, P., Desai, T. A., & Goldspink, P. H. (2015). Localized delivery of mechano-growth factor E-domain peptide via polymeric microstructures improves cardiac function following myocardial infarction. Biomaterials, 46, 26-34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.12.046
- Zabłocka, B., Goldspink, P. H., Goldspink, G., & Górecki, D. C. (2012). Mechano-growth factor: an important cog or a loose screw in the repair machinery? Frontiers in Endocrinology, 3, 131. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2012.00131
- Alagaratnam, S., Yang, S. Y., Loizidou, M., Fuller, B., & Ramesh, B. (2019). Mechano-growth factor expression in colorectal cancer investigated with fluorescent gold nanoparticles. Anticancer Research, 39(4), 1705-1710. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.13224
- McVeigh, J., Chandler, M., & Yarwood, G. A. (2023). Exercise and drugs performance-enhancing within and the the. The Body in the Mind: Exercise Addiction, Body Image and the Use of Enhancement Drugs, 4(7), 121.5. Veronese, F. M., & Pasut, G. (2005). PEGylation, the art to deliver. Drug Discovery Today, 10(21), 1451-1458. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6446(05)03584-0
- Zabłocka, B., Goldspink, P. H., & Goldspink, G. (2008). Mechano-growth factor (MGF) and tissue repair and regeneration. Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility, 29(4-5), 187-195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-008-9133-6
- Dluzniewska, J., et al. (2005). MGF and IGF-1 effects on muscle satellite cells. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 94(5-6), 587-594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-005-1386-8
- Peña, J. R., et al. (2012). MGF peptide neuroprotection after ischemic brain injury. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 90(7), 1469-1477. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.23078
- Goldspink, G. (2005). MGF and muscle hypertrophy. Journal of Physiology, 567(Pt 1), 1-3. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2005.088867
For more information on Mechano Growth Factor please visit Pubmed.
| Weight | 0.0099 lbs |
| Appearance | Fine White Lyophilized Powder |
| Residue Sequence | Tyr-Gln-Pro-Pro-Ser-Thr-Asn-Lys-Asn-Thr-Lys-Ser-Gln-Arg-Arg-Lys-Gly-Ser-Thr-Phe-Glu-Glu-Arg-Lys |
| Solubility | 100 µg/mL sterile diluent (distilled de-ionized water) |
| Source | Biosynthetic production |
| Stability | Lyophilized protein is to be stored at -20°C. It is recommended to divide the remaining reconstituted peptide into multiple vials so as to avoid a cycle of freezing and thawing. Reconstituted protein can be stored at 4°C. |
| Molar Mass | 2888.16 g/mol |
| Molecular Formula | C121H200N42O39 |
| MG | 2 MG |
| Terms | This product is sold for research/laboratory usage only. No other uses are permited. |
Additional information
| Weight | .03125 lbs |
|---|