-
×
 NAD+ 500mg
1 × $99.99
NAD+ 500mg
1 × $99.99
NEW
GHK-Cu 50mg
$49.99
You save
This product is intended as a research chemical only. This designation allows the use of this chemical strictly for in-vitro laboratory testing and experimentation. Human or veterinary use is strictly forbidden. This product is not a drug, food or cosmetic and may not be misbranded, mislabeled or misused as such.
Description


Buy GHK-Cu Copper Peptide at Loti Labs
Copper peptides research is an exciting area of study with many molecular mechanisms to be uncovered across multiple disciplines. When researchers want to buy GHK-Cu copper peptide for their lab work, the quality and purity of the compound directly impacts experimental results and data reliability. Understanding the molecular properties, research applications and sourcing of this tripeptide complex is key to advancing scientific knowledge in cellular biology and tissue research.
GHK-Cu Molecular Structure
The GHK-Cu copper peptide is a precisely defined molecular complex with specific structural properties that researchers must verify when working with the compound. This tripeptide is composed of glycine, lysine and histidine amino acids chelated with copper ions to form a stable research compound.
Molecular Specifications:
- Amino Sequence: Glycine-Histidine-Lysine-Cu2+
- Molecular Formula: C14H24N6O4Cu
- Molecular Weight: 411.93 g/mol
- PubChem CID: 91882201
- CAS Number: 89030-95-5
The copper part of the peptide is critical to its stability and biological activity in the lab. Research shows that the copper ions bind primarily to the imidazole side chain of the histidine residue to form a stable complex for lab use. Researchers must verify these molecular specifications to ensure consistent experimental conditions and reproducible results.
Mechanism of Action in Research
Lab research has shown that GHK-Cu copper peptide has multiple mechanisms of action that make it useful for various research applications. The compound affects cellular processes has been documented in many peer reviewed studies so researchers have a well characterised tool to study tissue biology and cellular mechanisms.
Research shows the peptide stimulates collagen synthesis pathways by activating fibroblast and increasing production of essential proteins. Studies show the copper part acts as a cofactor in enzymatic processes that support protein formation, making it particularly useful for researchers studying tissue engineering and wound healing mechanisms.
Gene expression studies have shown the peptide affects over 4,000 genes related to cellular repair, inflammation modulation and oxidative damage protection. This broad genetic effect makes GHK-Cu copper peptide useful for researchers studying aging, cellular stress responses and tissue regeneration mechanisms.The compound has anti inflammatory effects in the lab with research showing reduced expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-alpha and IL-6. Research also shows increased angiogenesis through stimulation of growth factors like VEGF and FGF, giving researchers insight into blood vessels formation and vascular biology.
Research Studies and Lab Applications
Since its discovery in human plasma in 1973 by Dr. Loren Pickart, GHK-Cu has been studied across multiple research areas. Lab research has provided valuable data on timeframes for observable changes in various experimental models to help researchers design their study protocols.
Research shows initial cellular changes can be seen within 2-4 weeks in the right experimental models, while significant collagen production takes 8-12 weeks. Maximum anti aging related changes in research models are generally seen with 3-6 months of consistent application. Hair growth research shows noticeable changes may take 4-6 months to assess, while wound healing research can show changes within days to weeks depending on the experimental model and severity parameters.
Key Research Findings:
| Research Area | Timeline for Observable Changes | Key Mechanisms |
|---|---|---|
| Wound Healing | Days to weeks | Tissue regeneration, angiogenesis |
| Skin Firmness Studies | 2-4 weeks initial, 8-12 weeks significant | Collagen synthesis, elasticity |
| Hair Growth Research | 4-6 months | Follicle cycle modulation |
| Gene Expression | Immediate to several weeks | DNA repair, inflammation modulation |
The peptide’s wound healing through tissue formation has made it very useful for researchers studying regenerative medicine applications. Research shows the compound attracts key immune cells like macrophages and mast cells which are involved in tissue repair processes.
Storage and Safety Considerations for Lab
Proper storage protocols are important when researchers buy GHK-Cu copper peptide to maintain molecular integrity and get reliable results. The compound requires specific storage conditions to prevent degradation and remain useful for research over time.
GHK-Cu products should be stored in cool, dark conditions away from direct light and heat sources. Research shows exposure to high temperatures or UV light can compromise the copper binding and reduce the peptide’s stability. For long term storage, storage temperatures between 2-8°C is generally recommended.Lab safety protocols require careful handling to prevent contamination and researcher safety. The compound should be kept away from incompatible chemicals, especially those that can interfere with copper binding or cause oxidative changes. Research settings should verify proper ventilation and PPE when handling the material.
When conducting experiments, researchers should not combine GHK-Cu with certain compounds that can reduce its stability or effectiveness. Research shows vitamin C, retinol and alpha hydroxy acids can interfere with the copper peptide’s action and affect experimental outcomes. Scientists should consult literature and do compatibility studies when designing multi-component research protocols.
Researchers doing oral studies should monitor for copper related effects in their models. High concentrations can cause gastrointestinal or systemic changes that can confound research results. Topical applications in research models should not touch eyes and mucous membranes to prevent irritation or redness.
Why Buy from Loti Labs
Research institutions and scientists looking to buy GHK-Cu copper peptide need suppliers that can provide verified quality, consistent purity and reliable delivery. Loti Labs offers multiple advantages that support rigorous scientific investigation and reproducible results.
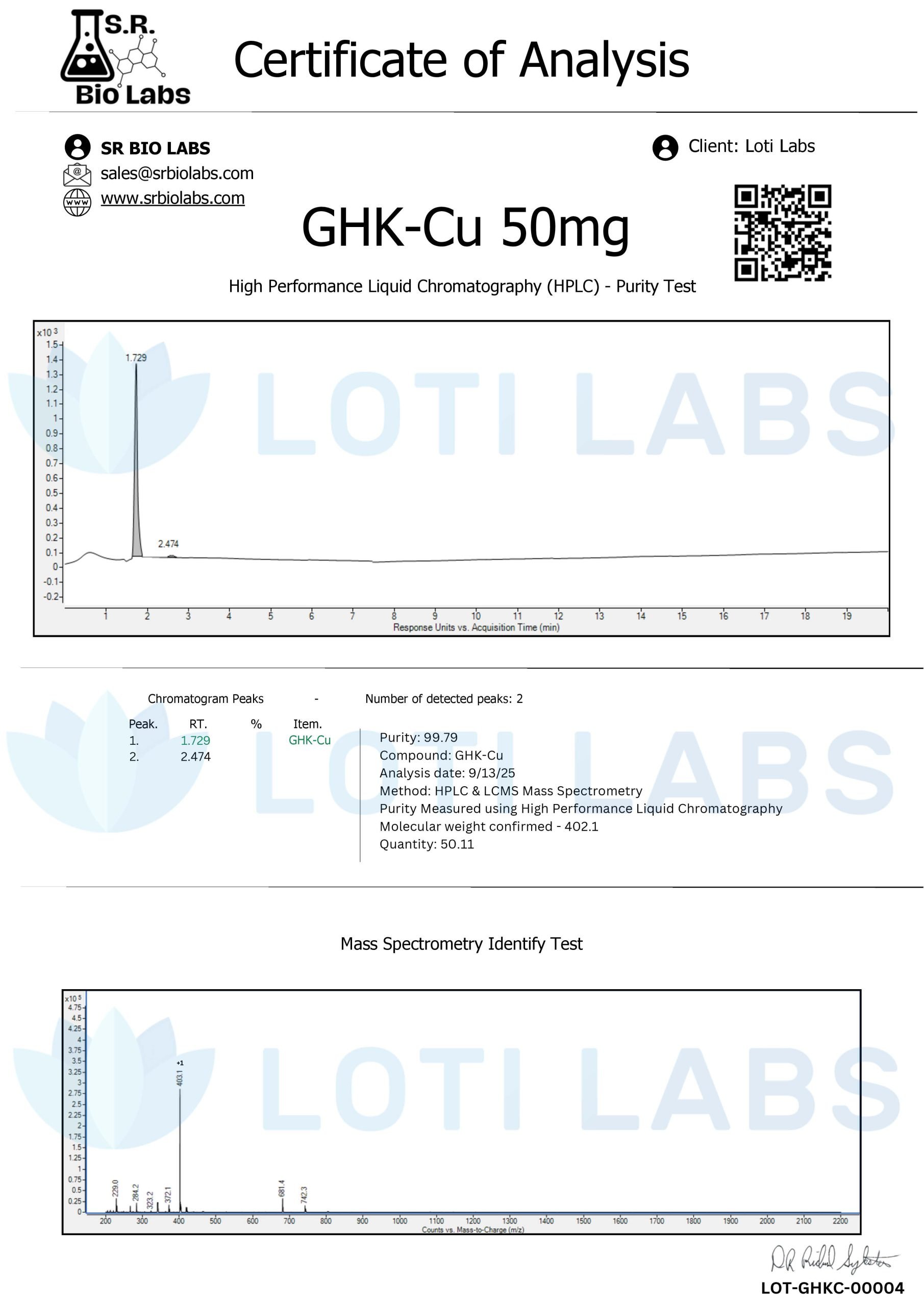
Our GHK-Cu copper peptide products undergo thorough quality control testing to verify molecular integrity and copper binding efficiency. Each batch is third-party tested using HPLC to confirm purity and molecular composition. This verification process ensures researchers get materials that meet their experimental requirements and produce consistent results across multiple studies.
Quality Assurance:
- High-purity GHK-Cu with 99%+ purity
- GMP certified manufacturing
- Rigorous verification protocols for molecular stability and bioactivity
- Temperature controlled storage and shipping
Loti Labs Products are for Research Use Only
All products from Loti Labs, including GHK-Cu copper peptide, are for research use only. This designation ensures compliance with regulations and supports the scientific community’s need for research compounds.
The research use only classification allows scientists to use GHK-Cu peptide for in-vitro lab testing and controlled experiments. This designation supports academic research, pharmaceutical development and biotechnology research while complying with regulations.
Human or veterinary use is strictly prohibited under this classification. These products are not intended for therapeutic use and should not be used outside of lab environments. Researchers must ensure their protocols comply with institutional guidelines and regulations for research compound use.The peptide allows researchers to study cellular mechanisms, tissue biology and molecular pathways without crossing into areas that would require different regulatory classifications. This way scientists can advance their knowledge of copper peptide without going outside the research boundaries.
Loti Labs Shipping Policy
Timely delivery is important for research continuity and project timelines. Loti Labs offers same day shipping for orders placed before 1pm EST Monday through Friday so researchers can get the materials they need when they need them.
Orders placed after 1pm EST or on weekends will be shipped the next business day to maintain consistent delivery schedules for researchers’ experimental planning. This shipping policy ensures research projects stay on track and lab schedules are not disrupted by supply delays.
Satisfaction Guarantee
Quality assurance goes beyond product specifications to customer satisfaction with research outcomes. Loti Labs offers 30-day satisfaction guarantee on all products. Researchers can return any unopened products for a full refund of the purchase price.
This guarantee shows confidence in product quality and gives researchers confidence when introducing new compounds into their protocols. The policy supports scientific investigation by reducing the financial risk of exploring new research directions or trying different suppliers.
Third Party Testing of Every Batch
Every batch of GHK-Cu peptide sold by Loti Labs is third-party tested using HPLC to ensure product purity and accuracy. This independent verification process gives researchers confidence in the molecular composition and quality of their research materials.
The testing protocols verify copper binding efficiency and molecular integrity to ensure each batch meets the concentration levels and structural characteristics required for reliable research outcomes. This verification process supports reproducible results and helps researchers trust their data.
Quality control extends to packaging and storage protocols that maintain compound stability from manufacturing to delivery. Temperature controlled shipping and appropriate packaging materials ensure the GHK-Cu copper peptide arrives ready to use in research applications.
Research shows batch-to-batch consistency is crucial for reproducible scientific results especially when doing long term studies or multi-phase research. The testing protocol ensures researchers can compare results across different timeframes and maintain data integrity throughout their research.
When scientists buy GHK-Cu copper peptide from Loti Labs they get materials that have been verified for molecular accuracy, stability and purity. This quality assurance supports the advancement of scientific knowledge and ensures research investments produce publishable results that contribute to the understanding of copper peptide biology and cellular mechanisms.With molecular verification, regulatory compliance and customer support Loti Labs is your go to partner for research on GHK-Cu copper peptide. Whether you are studying wound healing pathways, anti aging mechanisms or cellular response to copper peptides researchers can trust consistent high quality compounds to support their research and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in this area of biology.
Additional information
| Weight | .06250 lbs |
|---|