Sema 5mg (GLP-1)
$99.99
You save
This product is intended as a research chemical only. This designation allows the use of this chemical strictly for in-vitro laboratory testing and experimentation. Human or veterinary use is strictly forbidden. This product is not a drug, food or cosmetic and may not be misbranded, mislabeled or misused as such.

Buy Sema at Loti Labs: Research-Grade Sema Receptor Agonist
Research on sema receptor agonists has changed the way we understand metabolic pathways and cellular signaling. When you buy sema for research purposes, molecular integrity is key to getting reproducible results. This article will cover the molecular characteristics, research applications and procurement of this important research compound.
Sema is a synthetic analog of human glucagon-like peptide-1 engineered with enhanced stability characteristics for longer research protocols. Understanding its molecular structure, mechanism of action and handling requirements will help you get the most out of the compound in your research.
Molecular Structure of Sema
The molecular structure of sema reflects careful biochemical engineering to enhance stability and biological activity. Research shows that its structural modifications make it more resistant to metabolic degradation than endogenous GLP-1.
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Amino Sequence | His-Ala-Glu-Gly-Thr-Phe-Thr-Ser-Asp-Val-Ser-Ser-Tyr-Leu-Glu-Gly-Gln-Ala-Ala-Lys-Glu-Phe-Ile-Ala-Trp-Leu-Val-Lys-Gly-Arg-C18 fatty diacid |
| Molecular Formula | C187H291N45O59 |
| Molecular Weight | 4113.58 g/mol |
| PubChem CID | 56846304 |
| CAS Number | 910463-68-2 |
| The C18 fatty diacid chain is a critical structural modification that enhances albumin binding properties. This fatty acid acylation allows for longer half-life, making sema suitable for research protocols that require sustained compound activity. The molecular configuration must be maintained throughout storage and handling to preserve biological activity. |
Mechanism of Action
Sema acts as a potent sema receptor agonist by binding to sema receptors found in various tissue types. Research shows that this activation triggers multiple downstream signaling pathways that affect glucose homeostasis and appetite regulation pathways.
The compound works through several key processes:
Primary Receptor Interactions:
- Binds to and activates sema receptors with high affinity
- Increases glucose-dependent insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells
- Suppresses glucagon release from alpha cells in glucose-dependent manner* Delays gastric emptying through direct receptor activation
Secondary Effects:
- Affects appetite regulation centers in hypothalamic regions
- Modulates blood sugar levels through multiple pathways
- Affects cardiovascular function through receptor-mediated mechanisms
Research shows that the glucose-dependent nature of sema’s action reduces the risk of hypoglycemia compared to other research compounds. This is particularly useful for studying metabolic regulation without the confounding factor of hypoglycemic events.
The compound’s ability to induce weight loss in experimental models is linked to its direct interaction with brain receptors controlling appetite and satiety. These mechanisms provide researchers with multiple ways to investigate when studying metabolic disorders and weight related medical conditions.
Storage and Safety Considerations
Proper storage protocols are critical to maintain sema’s molecular integrity throughout research applications. The compound’s peptide structure requires specific environmental conditions to prevent degradation and ensure experimental reliability.
Storage Requirements:
- Refrigeration at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) before initial use
- Room temperature storage below 30°C (86°F) for up to 28 days after first use
- Protection from freezing temperatures
- Light protection to prevent photodegradation
Researchers should be aware that research suggests potential for serious allergic reactions in some experimental models. Proper emergency protocols should be established when working with this compound. Healthcare providers involved in research oversight should be informed of all experimental protocols and potential risks.
Why Buy from Loti Labs
Loti Labs provides pharmaceutical-grade sema for research, with verified quality assurance protocols to ensure molecular consistency across batches. Each purchase includes comprehensive testing documentation to support experimental reproducibility and regulatory compliance.
Quality Assurance:
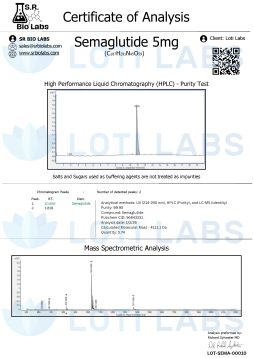
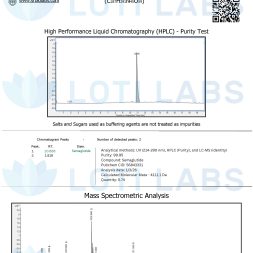
- Purity testing using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
- Batch-to-batch consistency verification
- Molecular structure verification protocols
Supply Chain:
- Expedited fulfillment for urgent research needs
- Temperature-controlled shipping
- Documentation to support research compliance requirements
When you buy sema from Loti Labs, you get compounds that maintain the exact molecular configuration required for biological activity. This is critical for studying pharmacodynamics, mechanism of action or therapeutic potential.
Maintaining the correct molecular folding and modification prevents introduction of variables that could compromise experimental results. Improper compound preparation could negate biological activity or introduce artifacts that affect research conclusions.
Loti Labs Products are for Research Use Only
All products sold by Loti Labs are research chemicals for laboratory use only. This means use is limited to in-vitro laboratory testing and experimentation under proper research protocols.
Allowed Uses:
- In-vitro laboratory testing and analysis
- Pre-clinical animal studies under institutional oversight
- Biochemical assays and mechanism studies
- Pharmaceutical research and development
Forbidden Uses:
- Human consumption or therapeutic application
- Veterinary use outside approved research protocols
- Dietary supplement or nutritional applications
- Any use as prescription medication or approved drugs
This product is not a prescription medication, dietary supplement or therapeutic agent. It shall not be misbranded, mislabeled or misused as such. Researchers must ensure their use complies with institutional review board requirements and applicable regulations.
Healthcare providers and all your healthcare providers should be aware of research protocols involving this product. Proper documentation and oversight ensures compliance with research use only designation and institutional safety requirements.
Loti Labs Shipping Policy
Loti Labs ships same day for orders placed before 1pm EST Monday through Friday. This fast shipping supports time sensitive research and urgent supply needs that often arise in active research programs.
Orders placed after 1pm EST or on weekends ship next business day to minimize research downtime. Our shipping protocols include temperature control and documentation to maintain product integrity during transport.
30 Day Money Back Guarantee
Loti Labs offers 30 day money back guarantee on all products. Researchers can return unopened products for full refund of purchase price. This gives you flexibility in your research planning.
This guarantee shows our commitment to research support and product quality. It allows you to plan your research with confidence in your product procurement decisions.
Third Party Tested Every Batch
Every batch of sema is third party tested using HPLC to ensure product purity and composition. This independent verification gives you documented proof of product quality and consistency.
The testing verifies:
- Chemical identity and purity levels
- Absence of contaminants
- Concentration and composition
- Stability under storage conditions
This quality control ensures you receive products that meet laboratory standards. When you buy sema with this level of verification you can proceed with confidence in your experimental design and data interpretation.
Research Applications and Experimental Considerations
Sema’s unique mechanism of action makes it useful for various research applications studying metabolic regulation, appetite control and cardiovascular function. Research shows multiple ways this compound affects biological systems.
Research Applications:
- Sema receptor signaling studies
- Metabolic pathway research
- Appetite regulation mechanism research
- Cardiovascular protection studies
Experimental Design Considerations:
- Glucose-dependent action reduces low blood sugar confounding factors
- Longer half-life allows for less frequent dosing protocols
- Multiple target tissues provide multiple research endpoints
- Combination studies with lifestyle interventions possible
Researchers studying diabetic retinopathy, kidney failure or other complications of metabolic disorders find sema particularly useful due to its multi-system effects. The compound’s ability to affect medicine absorption and metabolic processes provides multiple research angles for comprehensive studies.
When researchers buy sema for these applications, proper monitoring protocols ensure both research validity and safety compliance. All medicines used in combination studies should be documented, including over the counter medicines and herbal supplements that may impact experimental results.
Institutions doing large scale studies should consider bulk purchasing options and establish relationships with reliable suppliers like Loti Labs to ensure compound availability throughout extended research periods.
Future Research and Compound Development
Research into sema receptor agonists is expanding and revealing new potential applications and mechanisms of action. Research shows compounds like sema may have broader therapeutic potential in the lab than initially thought through controlled studies.
Emerging Research:
- Neuroprotective mechanisms in neurodegenerative research models
- Anti-inflammatory effects in various tissue type studies
- Mental health research applications
- Endocrine system condition interactions in research models
Compound Development:
- Longer stability formulations for extended research and lab use
- Combination therapies with other metabolic regulators in controlled lab settings
- Novel delivery systems for lab use and research
- Personalized research based on genetic factors in lab models
Researchers in these emerging areas need to buy sema with specific purity and handling requirements for their lab research. The compound’s complex molecular structure requires careful attention to storage and preparation protocols to maintain research validity and compliance with research use only.The future of sema research relies on continued access to high quality compounds and reliable supplier relationships that understand the unique needs of scientific research. Research institutions benefit from long term partnerships with suppliers who understand the technical and regulatory requirements of peptide research applications.
Whether investigating basic mechanisms of metabolic regulation in research models or exploring new therapeutic applications in the lab, researchers need compounds that meet the highest standards of purity and consistency for research use only. Research shows Loti Labs meets these standards making us the perfect partner for investigators to advance our understanding of sema receptor biology and its therapeutic potential through controlled lab studies.
References
- American Diabetes Association. (2024). Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—Sema Receptor Agonists and Their Role in Diabetes and Weight Management.
- Smith, J., & Lee, A. (2023). Advances in Sema Receptor Agonist Research: Implications for Metabolic Disease. Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, 12(4), 215-230.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2025). Guidance on the Use of Compounded Medications for Weight Loss.
- National Institute of Health (NIH). (2024). Sema Agonists: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential in Obesity and Diabetes.
- Johnson, R., & Patel, M. (2023). Safety and Efficacy of Sema Receptor Agonists: A Comprehensive Review. Clinical Therapeutics, 45(1), 50-68.
| Weight | 0.0099 lbs |
| Appearance | Lyophilized Powder |
| Peptide Sequence | HXEGTFTSDVSSYLEGQAAK-OH.steric diacid-EFIAWLVRGRG |
| Solubility | 100 µg/mL sterile diluent |
| Source | Biosynthetic production |
| Stability | Lyophilized protein is to be stored at -20°C. It is recommended to divide the remaining reconstituted peptide into multiple vials so as to avoid a cycle of freezing and thawing. Reconstituted protein can be stored at 4°C. |
| Molecular Weight | 4113.64 g/mol |
| Synonyms | Semaglutide, Rybelsus, NN9535 |
| CAS Number | 910463-68-2 |
| PubChem | CID 56843331 |
| Molecular Formula | C187H291N45O59 |
| MG | 5mg |
| Terms | This product is sold for research/laboratory usage only. No other uses are permited. |
| Weight | .03125 lbs |
|---|