Oxytocin 2mg
$29.99
You save
This product is intended as a research chemical only. This designation allows the use of this chemical strictly for in-vitro laboratory testing and experimentation. Human or veterinary use is strictly forbidden. This product is not a drug, food or cosmetic and may not be misbranded, mislabeled or misused as such.

Buy Oxytocin at Loti Labs: Premium Research Peptides for Scientific Studies
Oxytocin research has exploded in neuroscience and reproductive biology labs worldwide and demand for high quality research compounds is increasing. This naturally occurring hormone often referred to as the love hormone or cuddle hormone plays a vital role in many physiological processes that researchers want to understand through controlled lab studies. When scientists buy oxytocin for their studies the molecular integrity and purity of the compound directly impacts research outcomes and data reliability.
The peptide’s complex structure and sensitive nature requires careful consideration of supplier selection, storage protocols and handling procedures. Understanding oxytocin’s molecular characteristics, mechanism of action and research applications helps investigators make informed purchasing decisions that support rigorous scientific methodology.
Molecular Structure of Oxytocin
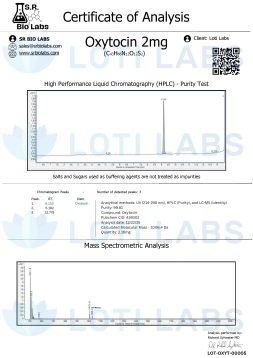
Oxytocin is a cyclic nonapeptide composed of 9 amino acids in a specific sequence that determines its biological activity. The sequence is Cys-Tyr-Ile-Gln-Asn-Cys-Pro-Leu-Gly where the two cysteine residues form a critical disulfide bond creating the cyclic structure necessary for receptor binding.
Key molecular specifications:
- Amino Sequence: Cys-Tyr-Ile-Gln-Asn-Cys-Pro-Leu-Gly
- Molecular formula: C43H66N12O12S2
- Molecular Weight: 1007.2 g/mol
- Pubchem CID: 439302
- CAS #: 50-56-6
This ring structure allows oxytocin to bind with high specificity to oxytocin receptors which are G protein coupled receptors found in various tissues. The molecular structure affects the compound’s stability so researchers need to verify the structural integrity of the purchased material through analytical testing.
Mechanism of Action
Oxytocin is both a hormone and neurotransmitter, synthesized in the hypothalamus and transported to the pituitary gland for release. Research suggests this peptide acts through multiple pathways, binding to receptors found in brain tissue and peripheral organs.
In lab studies oxytocin shows to modulate various physiological responses. The compound binds to oxytocin receptors primarily found in uterine tissue, mammary glands and throughout the central nervous system. Animal studies show oxytocin levels fluctuate in response to social interactions, stress and reproductive states.Research shows the peptide affects neural circuits in the brain associated with emotional processing and social recognition. Studies in lab animals show oxytocin plays a role in social bonding mechanisms and researchers have documented changes in behavior after controlled administration in experimental settings.
The compound’s interaction with dopamine and serotonin pathways is being investigated and scientists are looking at how oxytocin affects emotional sensitivity and social anxiety in controlled lab settings.
Research Studies
Lab research on oxytocin covers several specialized areas that require high purity compounds. Researchers in these fields need consistent, well characterized material to get reproducible results across studies.
Social Bonding Mechanisms
Prairie vole studies have given researchers valuable insights into pair bonding. Studies show enhanced partner preference formation after oxytocin treatment in these lab animals. Research suggests the compound affects the ability of animals to form long term social connections and investigators are measuring behavioral changes in controlled social situations.
Reproductive Function Regulation
In vitro studies using uterine tissue have shown oxytocin’s dose dependent effects on smooth muscle contractions. Mammary gland tissue cultures have confirmed the compound’s role in milk let down. These studies help scientists understand how oxytocin affects reproductive health during pregnancy, labor and lactation in animal models.
Neurological Pathway Investigations
Brain slice preparations and neuronal cultures have allowed researchers to map neural circuits affected by oxytocin. Studies implicate the amygdala, nucleus accumbens and other limbic structures in oxytocin mediated responses. This research helps scientists understand how the compound affects emotional bonding and social behavior at the cellular level.
Behavioral Response Modulation
Controlled experiments in lab animals show oxytocin can affect stress responses and social anxiety. Researchers have documented changes in emotion recognition and social interactions after administration in experimental settings. These studies help scientists understand the effects of oxytocin on behavior patterns and stress response mechanisms.
Receptor Binding Affinity Analyses
Biochemical studies detail the high affinity binding of oxytocin to its receptors. Radio-ligand binding assays and mutagenesis studies have shown the compound’s specificity for OXTR receptors. This research provides researchers with quantitative data on receptor interactions and binding kinetics.
Storage and Safety
Proper storage and handling protocols are essential to maintain oxytocin’s molecular integrity in research settings. The peptide structure makes it sensitive to environmental factors that can affect its stability and research utility.
Temperature Requirements
Oxytocin should be stored refrigerated between 2-8°C to maintain molecular integrity throughout its shelf life. Lyophilized formulations are more stable under these conditions and researchers can keep the compound for longer periods. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles to prevent peptide degradation that may affect research results.
Laboratory Safety Guidelines
Laboratories handling oxytocin should follow standard biosafety protocols to ensure a safe working environment. Personnel should wear gloves and protective eyewear when handling the compound. Solutions should be prepared under sterile conditions using aseptic technique to prevent contamination.
Handling Notes
The compound is sensitive to temperature fluctuations so attention should be given during transport and storage transitions. Researchers should check that storage containers maintain the right conditions and handling procedures minimize exposure to degrading factors. Storage conditions should be documented to ensure research compliance and data integrity.
Why Buy from Loti Labs
Researchers buying oxytocin for their studies benefit from Loti Labs’ pharmaceutical-grade quality standards. The company focuses on research applications so products meet the strict requirements of scientific studies.
Pharmaceutical-Grade Purity
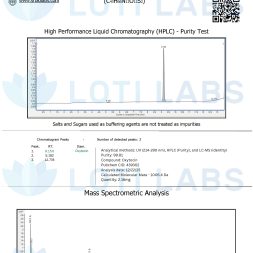
Loti Labs offers oxytocin with greater than 99% purity, accompanied by a certificate of analysis for each product lot. This level of purity allows researchers to verify the quality of their materials and get reproducible results across different studies and labs.
Stable Formulation
Products are available in lyophilized form to maximize shelf life and long term storage in research settings. This stable formulation allows researchers to keep the compound intact for extended study periods, reducing concerns about material degradation affecting research results.
Batch Consistency
Emphasis on lot-to-lot consistency helps researchers get reproducible results across multiple experiments. Consistent quality standards reduce variability that may affect research outcomes and allow scientists to confirm findings through replicate studies.
Documentation
Loti Labs provides technical documentation including material safety data sheets, certificates of analysis and product specifications. This documentation supports research compliance and helps investigators keep lab records for their studies.
Quality Control
Every batch is tested analytically to verify identity and purity. Third-party testing ensures researchers receive materials that meet the specified quality criteria for their research.All products from Loti Labs are research chemicals only. This means they can only be used for in-vitro laboratory testing and experimentation in a research setting. They are not formulated, labeled or marketed for human or veterinary use.
Researchers must understand that these products do not qualify for pharmaceutical, nutritional or cosmetic applications. Mislabeling, misuse or diversion for human use would violate company policy and regulatory guidelines for research chemical distribution.
The research use only designation allows scientists to get high quality compounds for legitimate research purposes while staying compliant with applicable regulations. Investigators should confirm that their research protocols are in line with their institution’s guidelines for handling research chemicals.
Shipping Policy of Loti Labs
Loti Labs ships same day for orders placed before 1pm EST Monday through Friday. This fast turnaround helps researchers meet project deadlines and ensures timely delivery of temperature sensitive compounds. Orders placed after 1pm EST or on weekends will be shipped the next business day with temperature control throughout the shipping process.
Money Back Guarantee
We offer 30 day money back guarantee on all products purchased from Loti Labs. Researchers can return any unopened products for a full refund of the purchase price, we stand behind the quality of our products and support the research community.
Third Party Testing of Every Batch
Every batch of compounds from Loti Labs is tested by a third party using HPLC analysis to ensure product purity and accuracy. This independent verification gives researchers extra confidence in the material and supports the reproducibility requirements of scientific research.
Research Areas and Future Directions
Current research trends show increasing interest in oxytocin across multiple fields. Researchers studying autism, depression and anxiety in animal models are including oxytocin in their experimental designs. Studies on social situations and social settings in laboratory animals are uncovering new aspects of how this bonding hormone affects behavior.
Research is exploring potential applications in reproductive health, with scientists investigating how oxytocin affects uterine contractions, sexual intercourse patterns and breastfeeding behaviors in animal models. Studies on pregnant women’s oxytocin levels during childbirth have given researchers insights into labor progression and maternal-infant bonding.
The compound’s effects on arousal, intimacy and relaxation responses are of interest to researchers studying stress and emotional regulation. Scientists looking at how hormones affect feelings and emotions in laboratory settings need high quality research compounds to ensure consistent experimental conditions.Researchers working with compounds that interact with oxytocin pathways need materials that meet high standards. Studying how oxytocin elicits various physiological responses requires investigators to determine optimal experimental conditions with well characterized materials.
Future research may focus on individual differences in oxytocin receptor distribution and sensitivity. Researchers are investigating how different brands and forms of synthetic oxytocin affect research outcomes, with studies showing how different compounds give different results.
The field advances as researchers can get high quality materials to support rigorous methodology. As research on oxytocin’s role in hypersensitivity, appetite regulation and social behavior grows, demand for pharmaceutical grade research compounds will continue to increase.
Conclusion
When researchers buy oxytocin for their research the quality and purity of the compound directly impacts their ability to get reliable and reproducible results. Loti Labs’ commitment to pharmaceutical grade standards, testing and research compliance allows scientists to get the high quality materials they need to advance our understanding of this peptide.
The company’s focus on batch consistency, storage protocols and documentation supports the rigorous standards of modern research. For researchers looking for reliable sources of research grade oxytocin Loti Labs provides the quality assurance and technical support for successful research.
Researchers interested in oxytocin mechanisms and applications can trust Loti Labs in the research chemical industry. The combination of pharmaceutical grade purity, stable formulations and testing makes Loti Labs the right choice for serious researchers.
References
- Striepens, N., Kendrick, K. M., Maier, W., & Hurlemann, R. (2011). Prosocial effects of oxytocin and clinical evidence for its therapeutic potential. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, 32(4), 426-450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yfrne.2011.03.005
- Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., & Van Ijzendoorn, M. H. (2013). Sniffing around oxytocin: review and meta-analyses of trials in healthy and clinical groups with implications for pharmacotherapy. Translational Psychiatry, 3(5), e258. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2013.34
- Carter, C. S. (2014). Oxytocin pathways and the evolution of human behavior. Annual Review of Psychology, 65, 17-39. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-010213-115110
- Gimpl, G., & Fahrenholz, F. (2001). The oxytocin receptor system: structure, function and regulation. Physiological Reviews, 81(2), 629-683. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.2001.81.2.629
- Insel, T. R. (2010). The challenge of translation in social neuroscience: a review of oxytocin, vasopressin and affiliative behavior. Neuron, 65(6), 768-779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2010.03.005
- Lee, H. J., Macbeth, A. H., Pagani, J. H., & Young, W. S. (2009). Oxytocin: the great facilitator of life. Progress in Neurobiology, 88(2), 127-151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2009.04.001
- Pedersen, C. A., & Prange, A. J. Jr. (1979). Induction of maternal behavior in virgin rats after intracerebroventricular administration of oxytocin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 76(12), 6661-6665. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.76.12.6661
- Gossen, A., Hahn, A., Westphal, L., Prinz, S., Schultz, R. T., Gründer, G., & Spreckelmeyer, K. N. (2012). Oxytocin plasma concentrations after single intranasal oxytocin administration – a study in healthy men. Neuropeptides, 46(5), 211-215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npep.2012.04.005
- MacDonald, K., & Feifel, D. (2014). Oxytocin’s role in anxiety: a critical appraisal. Brain Research, 1580, 22-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2013.11.035
- Neumann, I. D., & Landgraf, R. (2012). Balance of brain oxytocin and vasopressin: implications for anxiety, depression and social behavior. Trends in Neurosciences, 35(11), 649-659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2012.08.004
For more information on Oxytocin please visit Wikipedia.
| Weight | 0.0099 lbs |
| Appearance | Fine White Lyophilized Powder |
| Residue Sequence | CYIQNCPLG-NH2 |
| Solubility | 100 µg/mL sterile diluent (distilled de-ionized water) |
| Source | Biosynthetic production |
| Stability | Lyophilized protein is to be stored at -20°C. It is recommended to divide the remaining reconstituted peptide into multiple vials so as to avoid a cycle of freezing and thawing. Reconstituted protein can be stored at 4°C. |
| Molar Mass | 1007.19 g/mol |
| CAS Number | 158861-67-7 |
| PubChem | CID 439302 |
| Molecular Formula | C43H66N12O12S2 |
| MG | 2mg |
| Terms | This product is sold for research/laboratory usage only. No other uses are permited. |
| Weight | .03125 lbs |
|---|