GW-501516 10mg/ml (30ml)
$59.99
You save
This product is intended as a research chemical only. This designation allows the use of this chemical strictly for in-vitro laboratory testing and experimentation. Human or veterinary use is strictly forbidden. This product is not a drug, food or cosmetic and may not be misbranded, mislabeled or misused as such.

Buy GW501516 Research Chemical: High-Purity PPARδ Agonist for Lab Use
Research into energy metabolism and lipid catabolism has shown that selective peroxisome proliferator activated receptors modulators are crucial in cell based studies. Scientists investigating metabolic pathways need access to high quality research chemicals that meet high purity standards and regulatory compliance. When you buy gw501516 for lab use the compound’s PPARδ agonist properties make it useful for studies of fatty acid oxidation, energy uncoupling and metabolic regulation in controlled lab environment.
GW501516 also known as cardarine in research community is a valuable tool for researchers studying energy metabolism and related cellular processes. The compound’s development history and subsequent research applications show it’s still relevant in research today, but all research should be done with caution and follow regulatory guidelines.
Molecular Structure of GW501516
Chemical Formula: C21H18F3NO3S2
Molecular Weight: 453.498 g/mol
CAS #: 317318-70-0
EC50: 1.1nM
Half-life: 16-24 hours
The molecular structure of GW501516 has a trifluoromethyl-substituted phenyl ring with two sulfur atoms, thiazole and ether functionalities. When you buy gw501516 it will appear as a white to beige powder and is light sensitive. The melting point is 134-136°C and the predicted boiling point is 584.5°C.
Lab studies have shown that GW501516 is soluble in DMSO up to 20 mg/mL and is chemically stable when protected from light and stored at -20°C for long term storage.
Mechanism of Action
GW501516 is a selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta (PPARδ) agonist with over 1,000 fold selectivity versus PPARα and PPARγ. Originally developed by GlaxoSmithKline in the 1990s this compound recruits coactivator PGC-1α to upregulate genes involved in energy expenditure proteins and activates AMP-activated protein kinase pathways in research models.Research has shown that GW501516 binds to PPARδ with a Ki of 1 nM and an EC50 of 1 nM, both high affinity and potency. When bound to PPARδ the compound recruits coactivators such as PGC-1α which upregulates genes involved in energy expenditure, metabolism and fatty acid oxidation.
Animal studies have shown that GW501516 treatment increases energy metabolism pathways and fatty acid oxidation especially in skeletal muscle cells. Studies suggest the compound provides insights into diet induced obesity and insulin resistance pathways in animal models. Research with animal studies have shown increase in high-density lipoprotein and decrease in very-low-density lipoprotein, effects on lipid profile in controlled studies.
However researchers should note that activation of PPARδ by GW501516 may also contribute to increased cell proliferation signals. A 2018 study showed that GW501516 increased growth of colitis-associated cancer in animal models via increased inflammation and upregulation of energy substrate transporters, so caution should be exercised in research settings.
Research Studies
GW501516 has been used in various research applications including lipid metabolism and fatty acid oxidation studies in skeletal muscle cells. Research has been focused on energy metabolism, mitochondrial biogenesis, cardiovascular health and metabolic syndrome protocols. Studies used 10mg daily for metabolic research while human clinical trials used 2.5mg to 18mg daily before discontinuation.
Primary Research Domains
| Research Area | Applications | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Lipid Metabolism | Fatty acid oxidation studies | Increased muscle cell fat utilization |
| Energy Metabolism | Mitochondrial biogenesis research | Enhanced energy expenditure pathways |
| Cardiovascular Research | Lipid profile investigations | Improved HDL/VLDL ratios in animal studies |
| Metabolic Syndrome | Insulin resistance studies | Protective effects against diet induced obesity |
Research has shown that GW501516 has profound effects on metabolism, studies have shown shift in substrate utilization from glucose to fatty acids. The compound is a valuable tool to dissect energy metabolism pathways and understand metabolic syndrome mechanisms in lab settings.
Researchers have used GW501516 to study regulatory networks of metabolic syndrome, mitochondrial function and exercise mimetics. Studies have shown the compound’s ability to stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis and upregulate proteins involved in energy expenditure makes it useful for research into obesity and type II diabetes mechanisms.More research is being done on the compound’s effect on cardiovascular health markers, animal studies have shown potential improvements in lipid profile that may be relevant to atherosclerosis research. However researchers should balance these findings with safety profile seen in long term animal studies.
Storage and Safety
Store GW501516 at room temperature in cool, dry conditions away from moisture. Protect from direct sunlight and temperature fluctuations to maintain stability. Use glass containers to prevent plasticizer leaching and contamination. GW501516 is not approved by FDA for human consumption, animal studies at 3mg/kg/day showed rapid cancer development in multiple organs, so proper laboratory handling protocols should be followed.
Storage Requirements
Proper storage of GW501516 is crucial to maintain compound integrity and research reliability. Store in a cool dry place at room temperature, protected from moisture and direct sunlight to avoid degradation. Temperature fluctuations and light exposure increase the risk of decomposition which may affect research results.
Store GW501516 in glass containers rather than plastic to prevent plasticizer leaching which may contaminate the compound and affect experimental results. Long term storage at -20°C is recommended for long term storage.
Safety Considerations
From a safety perspective GW501516 is not approved by FDA for human use under any circumstances. Animal studies have shown significant safety concerns, rodent studies at 3mg/kg/day showed rapid and aggressive cancer development in multiple organs including liver, bladder, stomach, skin, thyroid, tongue, testes, ovaries and uterus.
These findings emphasize the importance of strict laboratory protocols when handling and experimenting with GW501516. All use must be restricted to in-vitro research environments, with strict controls on exposure, labeling and waste disposal. The compound’s side effects profile including liver toxicity seen in animal studies requires appropriate safety measures and expert handling procedures.
Researchers should implement comprehensive safety protocols including proper ventilation, personal protective equipment and contamination prevention measures. The world anti doping agency has banned GW501516 since 2009 due to its misuse as a performance enhancement substance, but this does not affect its legitimate research applications when properly managed.
Why Buy from Loti Labs
Loti Labs offers GW501516 with 98% purity, tested in the laboratory. Our products are packaged in pharmaceutical grade containers with proper labeling and comes with documentation for research verification. We have transparent business practices with dedicated customer support and quality assurance protocols that exceed industry standards.
Quality Assurance
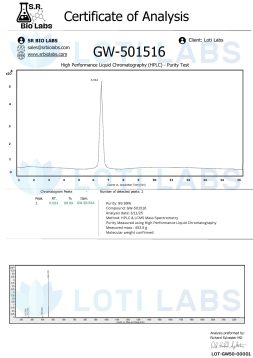
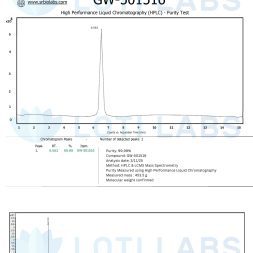
When you buy cardarine online from Loti Labs you get a great product that undergoes strict quality control. Each batch is third party tested, most often via HPLC, to verify purity and content. This analysis ensures you get consistent high quality material for your research.
We provide packaging in pharmaceutical grade, properly labeled containers to ensure safety, traceability and compliance to lab standards. Loti Labs promotes transparency in business practices by providing detailed documentation and supporting research verification processes that you need for your work.
Customer support and quality assurance protocols advertised by the company exceed industry standards so you can have confidence in your purchase. Our commitment to quality goes beyond initial delivery to ongoing support for research applications and technical inquiries.
Documentation and Verification
Every purchase comes with comprehensive documentation to support research verification and regulatory compliance. The detailed labeling and documentation provided helps you maintain proper chain of custody and ensure proper handling throughout your research.
Loti Labs is transparent in their business practices, providing detailed information about product specifications, testing protocols and quality measures. This helps you who need thorough documentation for your institutional review board and research protocols.
Products from Loti Labs are for Research Use Only
All products sold by Loti Labs are research chemical only. This means use of this compound is strictly for in-vitro laboratory testing and experimentation. Human or veterinary use is strictly forbidden. This product is not a food or cosmetic and may not be misbranded, mislabeled or misused as such. GW501516 has been banned by WADA since 2009 for competitive sports but remains legal for laboratory research applications.
Regulatory Compliance
The research use designation is a critical legal and regulatory distinction that you must understand. This means the compound is licensed solely for laboratory experimentation, quality control and in-vitro research applications. Any use outside of controlled laboratory procedures is prohibited and subject to enforcement actions.Since 2009 GW501516 has been on the WADA prohibited list for its misuse as an endurance agent in sports. Although it’s banned in competitive sports, it’s still available for legitimate research use when used according to regulatory guidelines.
Researchers should note that GW501516 is not a selective androgen receptor modulator, although it shares some research applications with such compounds. It works through different mechanisms, targeting peroxisome proliferator activated receptors instead of androgen receptor pathways.
Research Applications
Laboratory research using GW501516 should focus on metabolic pathways, energy regulation and cellular mechanisms rather than performance enhancement or weight loss applications. Researchers studying genes involved in metabolism, fat oxidation and energy uncoupling will find this compound useful for their research.
The compound’s effects on testosterone levels, heart disease markers and insulin resistance make it relevant for researchers investigating cardiovascular health and metabolic syndrome mechanisms. But all applications must be within approved research use guidelines and institutional review board protocols.
Studies show that proper research use of GW501516 can provide valuable insights into energy metabolism, lipid catabolism and cellular regulation mechanisms. Researchers must ensure their research complies with institutional guidelines and focus on advancing scientific knowledge rather than developing dietary supplements or performance enhancement applications.
Loti Labs Shipping Policy
Loti labs ships same day for orders placed before 1pm EST Monday through Friday. Orders placed after 1pm EST or on weekends will be shipped the next business day.
The company’s shipping policy ensures efficient delivery of research materials so you receive your order promptly. This logistics approach aims to maximize customer satisfaction and support research timelines while maintaining proper handling and packaging standards.
Shipping protocols include proper packaging to protect compound integrity during transport and comply with shipping regulations for research chemicals. The company’s commitment to fast delivery supports researchers who need timely access to materials for their research.
Money Back Guarantee
Loti Labs offers 30 day money back guarantee on all products purchased from us. Just return any unopened products to us for full refund of the purchase price of the unused products.
This guarantee gives you confidence in your purchase and reflects the company’s commitment to product quality and customer service. The guarantee is to ensure product quality, handling and the company’s support for research applications.You can buy with confidence knowing that unopened products can be returned within the specified timeframe. This policy is for budget conscious research environments and for researchers managing multiple project requirements.
Third Party Testing of Every Batch
Every product sold by Loti Labs is third party tested using HPLC to ensure product purity and accuracy. Our GW501516 is tested by US accredited laboratories with published results and comes with a certificate of analysis (COA) for each batch, guaranteeing minimum 98% purity.
Testing Protocols
The third party testing protocols used by Loti Labs ensures that you receive consistent high quality materials for your research. High performance liquid chromatography analysis provides detailed information about compound purity, content and potential contaminants that could affect your research results.
Each COA includes comprehensive data about the specific batch including purity percentages, testing methodologies and laboratory accreditation information. This documentation is for researchers who need detailed analytical information for their IRB and publication requirements.
Verification by US accredited laboratories provides additional assurance of testing quality and reliability. You can review published results and COA documentation to verify that the material meets your research requirements and institutional standards.
Quality Standards and Verification
The minimum 98% purity standard of Loti Labs exceeds many industry standards and is suitable for high quality research applications. This purity level ensures you can research with confidence in your material quality and consistency.
Batch specific documentation allows you to keep records for your research and supports reproducibility. The detailed analytical information provided with each batch helps you understand any variations between shipments and adjust your protocols accordingly.
The testing and documentation approach supports researchers in regulated environments or preparing materials for publication. Quality verification goes beyond initial testing to ongoing support for research applications and technical inquiries about specific batches.
Conclusion
Researchers studying energy metabolism, fatty acid oxidation and peroxisome proliferator pathways will find GW501516 to be a useful tool for their laboratory research. When you buy gw501516 from Loti Labs you get a thoroughly tested research chemical that meets high purity standards and comes with documentation to support your research goals.
The compound’s unique property as a PPARδ agonist and established research applications in metabolic studies make it an important addition to research laboratories studying cellular energy regulation. But researchers must adhere to research use only guidelines and implement proper safety protocols based on animal study findings.Loti Labs’ quality, third party testing and regulatory compliance gives researchers the confidence and reliability they need for their research. Our approach to quality assurance, customer service and documentation supports legitimate research while being compliant to regulations.
For researchers looking for high purity GW501516 for their metabolic research, Loti Labs has the quality, testing protocols and customer support for successful research outcomes. Contact us to discuss your research requirements, review COA documentation or learn how our quality assurance protocols can support your laboratory’s research goals.
References
- Tanaka T, et al. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ induces fatty acid β-oxidation in skeletal muscle and attenuates metabolic syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(26):15924–15929. https://www.pnas.org/content/100/26/15924
- Chen W, et al. A metabolomic study of the PPARδ agonist GW501516 for enhancing running endurance in Kunming mice. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9884. https://www.nature.com/articles/srep09884
- Fan W, et al. PPARδ promotes running endurance by preserving glucose. Cell Metab. 2017;25(5):1186–1193.e4. https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(17)30256-6
- Oliver WR Jr, et al. A selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta agonist promotes reverse cholesterol transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(9):5306–5311. https://www.pnas.org/content/98/9/5306
- Dressel U, et al. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta agonist, GW501516, regulates the expression of genes involved in lipid catabolism and energy uncoupling in skeletal muscle cells. Mol Endocrinol. 2003;17(12):2477–2493. https://academic.oup.com/mend/article/17/12/2477/2845332
- Magliano DC, et al. Short-term administration of GW501516 improves inflammatory state in white adipose tissue and liver damage in high-fructose-fed mice through modulation of the renin-angiotensin system. Endocrine. 2015;50(2):355–367. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12020-015-0567-1
- Van Wagoner RM, et al. Chemical composition and labeling of substances marketed as selective androgen receptor modulators and sold via the internet. JAMA. 2017;318(20):2004–2010. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2656319
- Burri L, et al. PPARα in liver and muscle. PPAR Res. 2010;2010:542359. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ppar/2010/542359/
- Leone TC, et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) is required for the fasting-induced down-regulation of lipogenic gene expression in the liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96(13):7473–7478. https://www.pnas.org/content/96/13/7473
- Kersten S, et al. PPARalpha is essential for adaptive response to fasting: the PPARalpha-null mouse. J Clin Invest. 1999;103(11):1489–1498. https://www.jci.org/articles/view/7984
- Coll T, et al. GW501516 activates PPARδ and prevents fatty acid-induced NF-κB activation and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle cells. Endocrinology. 2010;151(4):1560–1569. https://academic.oup.com/endo/article/151/4/1560/2423393
- Sahebkar A, et al. New PPAR agonists: potential treatment for atherogenic dyslipidemia and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2014;15(4):493–503. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1517/14656566.2014.866655
- Sprecher DL. Lipids, lipoproteins, and PPARδ. Am J Cardiol. 2007;100(11A):n20–n24. https://www.ajconline.org/article/S0002-9149(07)01889-6/fulltext
For more information on GW-501516 Cardarine please visit Wikipedia.
| Weight | 0.1875 lbs |
| Appearance | Viscous cloudy liquid |
| Stability | Room Temperature out of direct sunlight |
| Molar Mass | 453.498 |
| CAS Number | 317318-70-0 |
| Container | 30ml Bottle |
| Molecular Formula | C21H18F3NO3S2 |
| Concentration | 10mg per ML |
| Terms | This product is sold for research/laboratory usage only. No other uses are permited. |
| Weight | 0.156 lbs |
|---|