Gonadorelin 5mg
$49.99
You save
This product is intended as a research chemical only. This designation allows the use of this chemical strictly for in-vitro laboratory testing and experimentation. Human or veterinary use is strictly forbidden. This product is not a drug, food or cosmetic and may not be misbranded, mislabeled or misused as such.

Buy Gonadorelin at Loti Labs: Research Peptide for Scientific Studies
Research into reproductive physiology and endocrine function requires molecular tools, and gonadorelin is a key synthetic analog for studying gnrh pathways. As researchers continue to unravel the mechanisms of fertility, hormone regulation and related physiological processes, access to research chemicals becomes crucial for getting reliable, reproducible data.
When you buy gonadorelin from us, you get a synthetic decapeptide that mirrors the structure and function of endogenous gnrh. This is a research tool for scientists studying the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and its role in various biological processes.
Molecular Structure of Gonadorelin
Gonadorelin has a precise molecular structure that makes it a research compound. The amino sequence is pGlu-His-Trp-Ser-Tyr-Gly-Leu-Arg-Pro-Gly-NH2, same as natural gnrh.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C55H75N17O13 |
| Molecular Weight | 1182.311 g/mol |
| PubChem CID | 638793 |
| CAS Number | 34973-08-5 (Acetate salt), 33515-09-2 (Free base) |
This synthetic form has the critical structural elements for receptor binding and activation in experimental models. The short peptide chain makes it the shortest known releasing hormone, but its precise configuration allows direct binding to gnrh receptors on pituitary cells during research applications.
The gonadorelin acetate used in research is more stable and soluble than the free base form. The salt formation is crucial in maintaining compound integrity during storage and experimental preparation.
Mechanism of Action in Research
Gonadorelin is a gnrh agonist in experimental systems, binds to and activates gnrh receptors on pituitary cells. Research shows this interaction triggers a cascade of cellular events leading to the release of lh and fsh from the pituitary gland.The mechanism of action depends on the administration pattern in experimental models. Pulsatile exposure in research mimics natural hormone production pattern where hypothalamus releases gnrh every 90-120 minutes. This pulsatile stimulation maintains receptor sensitivity and continues to release lh and fsh in experimental systems.
Conversely, continuous exposure to gonadorelin in research models can lead to receptor downregulation and eventually suppress gonadotropin secretion. This dual response profile makes the compound useful for researchers to study both stimulatory and inhibitory effects on the reproductive axis.
Studies have shown that gonadorelin activates the same physiological pathways as endogenous hormone, making it a good analog to study normal and disrupted reproductive function in experimental models.
Research Studies and Applications
Gonadorelin has been used in many research applications to provide insights into reproductive physiology, endocrine function and related therapeutic targets. Researchers use this compound as both a diagnostic tool and experimental intervention.
Gonadorelin is useful in:
Fertility and Reproductive Research
- Studies of hypothalamic amenorrhea mechanisms
- Hypogonadism pathways
- Delayed puberty in experimental models
- Cryptorchidism in rats and other animal models
Hormone Recovery Research
- Hormone restoration after suppression therapy
- Natural hormone production recovery mechanisms
- Testosterone restoration in experimental models
Cancer Research Applications
- Prostate cancer cell proliferation
- Breast cancer hormone dependency
- Gnrh receptor expression in tumor cells
- Hormone dependent cancer growth
Neurodegenerative Research
- Hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis dysfunction
- Reproductive hormones and neurodegeneration
- Gnrh’s neuroprotective effects in experimental models
Diagnostic Research
- Pituitary function assessment
- Hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis integrity
- Hormone response after gonadorelin administration
Recent research has expanded to include studies on spermatogenesis in male animal models and ovulation in female research subjects. These studies provide valuable information on reproductive timing and fertility.Researchers working with men in experimental models have studied gonadorelin’s ability to stimulate endogenous lh production and preserve testicular function during hormone manipulation studies. This has important implications for reproductive physiology under different experimental conditions.
Storage and Safety
Proper storage and handling is crucial to maintain gonadorelin’s stability and researcher safety. The compound requires specific environmental conditions to preserve its biological activity and prevent degradation.
Storage:
- Unopened powder: -20°C for long term storage
- Reconstituted solutions: 2-8°C
- Use reconstituted material within manufacturer specified time frame
- Maintain cold chain integrity during shipping and storage transitions
Safety:
- Use personal protective equipment (gloves, lab coats, eye protection) when handling
- Work under fume hood when aerosolization risk exists
- Follow institutional guidelines for research chemical handling
- Maintain proper documentation and chain of custody
Reconstituted solutions should be used promptly to ensure maximum biological activity. The time frame depends on formulation and preservative content, so follow manufacturer’s recommendation for best results.
Why Buy from Loti Labs
Loti Labs provides researchers with high quality gonadorelin formulations for research use. Our quality assurance ensures that researchers receive products meeting purity standards for reproducible results.
Products:
- Gonadorelin acetate powder for reconstitution
- Pre-mixed solutions for research protocols
- Multiple concentrations to fit different experimental needs
- Consistent batch to batch quality for longitudinal studies
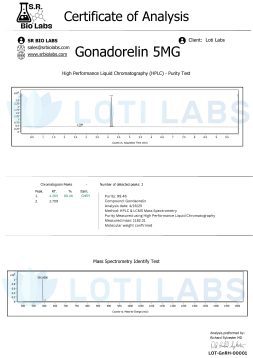
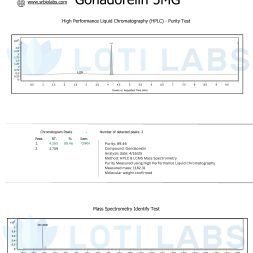
Quality Assurance: Every batch is tested by third party using hplc analysis. This external verification confirms product purity, peptide content and absence of contaminants that can affect experimental results.
Customer Support: Scientific support staff will guide you on product selection to help you choose the right formulation for your experimental requirements. This technical support ensures product performance in research applications.Manufacturing: Products are made to research specifications with attention to purity and concentration consistency to support reproducible results across multiple experimental sessions.
Loti Labs Products are for Research Use Only
All products sold by Loti Labs are designated “Research Use Only” (RUO), a legal classification that defines the use parameters. This designation allows use of these substances only for in-vitro laboratory testing and experimentation.
Important Restrictions:
- Human or veterinary use is strictly forbidden
- Not for prescription use
- Not for cosmetics or food additives
- Misbranding, mislabeling or misuse is prohibited
Research Context: These restrictions ensure researchers keep boundaries when working with experimental compounds. The RUO designation protects both researchers and institutions by defining acceptable use within research settings.
Legal Compliance: Researchers must have strict procedural controls to prevent accidental exposure, cross-contamination or misuse. Institutional review boards and safety committees usually oversee research chemical use protocols.
Shipping and Customer Satisfaction
Rapid Fulfillment: Loti Labs ships same day for orders placed before 1pm EST, Monday to Friday. Orders placed after this cut off or on weekends ship the next business day. This rapid fulfillment ensures temperature sensitive compounds like gonadorelin arrive at their destination potent.
Satisfaction Guarantee: 30 day satisfaction guarantee. Unopened products can be returned for full refund. This policy shows confidence in product quality and reduces risk for research institutions making large reagent investments.
Quality Control: Every batch sold is tested by third party to verify purity and concentration. This external validation gives researchers confidence in product specifications and supports reproducible results.
Ordering and Contact
Researchers interested in purchasing gonadorelin for research can contact Loti Labs for product information and ordering assistance. Our scientific support team can guide you on formulation selection and storage requirements for optimal results.
Ordering Process:
- Contact customer service to discuss research requirements
- Select formulation and concentration
- Verify institutional compliance with RUO guidelines
- Complete order and arrange deliveryWhen you buy gonadorelin from Loti Labs you get research chemicals tested and backed by quality assurance and customer support. This combination of product and service makes Loti Labs your go to partner for research in reproductive physiology and related fields.
The company’s commitment to high standards throughout manufacturing, testing and shipping ensures you receive products that will give you reliable and reproducible data in your research.
References
- Millar, R. P., Lu, Z. L., Pawson, A. J., Flanagan, C. A., Morgan, K., & Maudsley, S. R. (2004). Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptors. Endocrine Reviews, 25(2), 235–275. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2003-0023
- Plant, T. M. (2015). 60 YEARS OF NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY: The hypothalamo-pituitary-gonadal axis. Journal of Endocrinology, 226(2), T41–T54. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-15-0113
- Conn, P. M., & Crowley, W. F. Jr. (1994). Gonadotropin-releasing hormone and its analogs. Annual Review of Medicine, 45, 391–405. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.med.45.1.391
- Kakar, S. S., & Jabbour, H. N. (2016). Gonadotropin-releasing hormone and its analogs: Basic and clinical aspects. Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America, 45(4), 751–764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecl.2016.07.003
- Hohmann, J. G., & Plant, T. M. (1988). Pulsatile luteinizing hormone secretion in the male rhesus monkey: Effects of gonadotropin-releasing hormone pulse frequency and amplitude. Endocrinology, 122(1), 90–98. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo-122-1-906. Lahlou, N., & Gharib, S. (2015). Gonadorelin and its clinical applications. In Reproductive Endocrinology (pp. 123–134). Springer.
- Crowley, W. F., & Filicori, M. (1990). Clinical use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogs. Fertility and Sterility, 53(5), 743–754. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0015-0282(16)54206-6
- Millar, R. P. (2005). GnRHs and GnRH receptors. Animal Reproduction Science, 88(1-2), 5–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anireprosci.2005.05.014
- Kauffman, A. S., & Rissman, E. F. (2004). Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor regulation: Implications for reproductive function. Endocrine Reviews, 25(3), 272–290. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2003-0024
- Lahlou, N., & Gharib, S. (2018). Gonadorelin acetate in reproductive research: Applications and perspectives. Journal of Endocrinological Investigation, 41(9), 1021–1031. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-018-0895-6
| Weight | .03125 lbs |
|---|