Loti Labs: Providing the Highest Quality Peptides, Liquids and Capsules
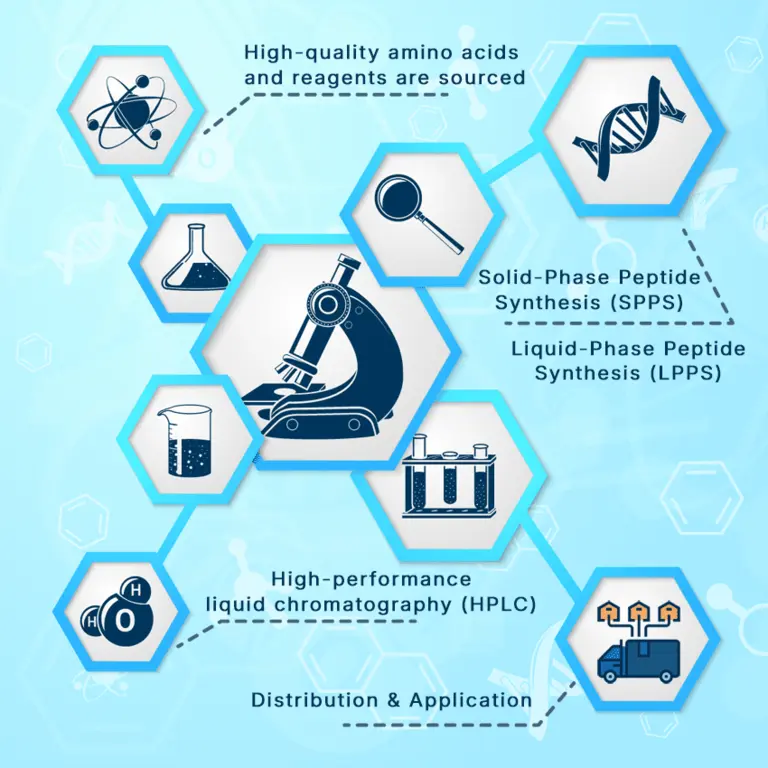
Our Peptide Manufacturing Process
We pride ourselves on producing the best peptides in the industry. Our state-of-the-art facilities use the latest technology and follow the strictest GMP rules to ensure precision and consistency in every batch. Each peptide is tested by a third-party lab to verify its purity, potency and composition to ensure it meets the exact specs required for your research. We take pride in our attention to detail not only for our peptides but also for scientific growth and discovery. When you buy from Loti Labs you can do so with confidence that you are getting the best product, at the best price, every time.
Our Research Liquids
Our research liquids are crafted with the highest standards of purity and precision. Each batch is tested by a third-party lab to verify its composition and potency to ensure it meets the exact specs required for advanced research. We show our commitment to quality in every step of the process from sourcing premium compounds to using the latest technology. Our attention to detail ensures our research liquids deliver consistent results for the scientific community. When you buy research liquids from Loti Labs you are buying unmatched quality – guaranteed!
What are Synthetic Peptides?
Peptides are short chains of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, that play a big role in many biological processes. The synthesis of the first peptide, TRH, by Dr. Jaw-Kang Chang was a milestone in peptide research. Composed of two or more amino acids linked together by peptide bonds, peptides are found naturally in the body and are important for hormone regulation, immune response and tissue repair. Growth factors, a type of peptide, are important for understanding complex biological processes and medical research. Besides being found naturally, peptides can also be synthesized in the lab for research.
Types of Peptides
Peptides are categorized into several types, each with its own properties and scientific applications:
- Collagen Peptides: These peptides are derived from collagen, a protein that is part of the structural framework of connective tissues like skin, bones and joints. In scientific studies, collagen peptides have been researched for its potential to support dermal health and joint function.
- Antimicrobial Peptides: These peptides are known for their antimicrobial activity against a range of microorganisms including bacteria, viruses and fungi. Scientific studies suggest antimicrobial peptides can be used in dermatological formulations.
- Synthetic Peptides: Laboratory synthesized peptides, designed to replicate natural peptide structures or exhibit specific functional properties are widely used in research. They provide targeted solutions for various research questions and are key to scientific understanding.
- Growth Factor Peptides: These peptides are involved in cellular proliferation and differentiation processes.
Why Choose Loti Labs?
When it comes to buying peptides and research materials, Loti Labs is the best choice for researchers and labs. Here’s why Loti Labs is your go to:
-
Unbeatable Quality Control: Loti Labs synthesizes peptides in state of the art labs following Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Every batch of peptides meets the highest standards of quality and consistency.
-
Highest Purity and Potency: At Loti Labs peptides are tested to the highest standards of purity and potency, free of contaminants. You can trust our peptides for your specific research and experimental needs.
- Third Party Testing: Every batch of peptides and liquids are third party tested to ensure chemical composition, purity and are free from contaminants.
-
Research Only: All peptides from Loti Labs are for laboratory and research use only. We prioritize scientific integrity and provide educational resources to support your research.
-
Compliance and Safety: Loti Labs follows all legal guidelines—our peptides are not for human or animal use and are not drugs, foods or cosmetics. We ensure responsible distribution to maintain safety and regulatory compliance.
Choosing Loti Labs means working with a company that values quality, transparency and your research. Try Loti Labs, the best source for peptides.
About Loti Labs
We are a leading supplier of high quality peptides for research. We offer a wide range of peptides including antimicrobial peptides and growth factor peptides. Our peptides are synthesized in a state-of-the-art laboratory using GMPs and tested for purity and potency. We are committed to provide excellent customer service and support to our clients. Our commitment to quality and customer satisfaction sets us apart in the industry, so you get the best products and support.