MOTS-c 10mg
$69.99
You save
This product is intended as a research chemical only. This designation allows the use of this chemical strictly for in-vitro laboratory testing and experimentation. Human or veterinary use is strictly forbidden. This product is not a drug, food or cosmetic and may not be misbranded, mislabeled or misused as such.

Buy MOTS-c at Loti Labs: Complete Research Guide
Research into mitochondrial derived peptides has revealed some amazing insights into cellular metabolism and energy homeostasis. Scientists looking to buy mots c for their research need compounds that meet high purity standards with full analytical documentation. MOTS-c, a 16 amino acid mitochondrial encoded peptide mots, is a must have research tool for studying metabolic regulation and aging in controlled environment.
The mitochondrial derived peptide mots c comes from the mitochondrial genome, specifically from the 12S rRNA gene’s open reading frame. Research shows this peptide mots c plays important roles in systemic metabolism, making it a valuable compound for researchers studying cellular metabolism and metabolic homeostasis.
Molecular Structure of MOTS-c
The derived peptide mots c has a precisely defined 16 amino acid sequence with arginine (Arg), tryptophan (Trp), glutamine (Gln), glutamic acid (Glu), glycine (Gly), tyrosine (Tyr), isoleucine (Ile), and phenylalanine (Phe). The full sequence is: arg trp gln glu-Met-gly tyr ile phe-Tyr-Pro-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg, a compact yet functional peptide.
Key Molecular Properties:
Property
Value
Amino Sequence
16 amino acid peptide with Arg, Trp, Gln, Glu, Gly, Tyr, Ile, and Phe
Molecular Formula
C97H146N30O32
Molecular Weight
2174.59 Daltons
PubChem CID
91758452
CAS Number
1360004-48-5
This mitochondria derived peptide is one of the mitochondrial derived peptides that researchers have found to come from the mitochondrial open reading frame. The molecular weight of 2174.59 Daltons puts mots c in the optimal range for cellular uptake and biological activity in experimental systems.
Mechanism of Action
mots c peptide acts as a key regulator of metabolic processes by interacting with the amp activated protein kinase pathway. Research shows that maintaining mitochondrial function requires coordination between nuclear genomes and mitochondrial derived signaling molecules like the mitochondrial derived peptide mots.Experimental studies show mots c treatment affects glucose metabolism through ampk activation. The peptide regulates nuclear gene expression by modulating the folate cycle and cellular metabolism pathways. Studies show mots c administration can improve insulin sensitivity in skeletal muscle tissue through increased glucose uptake mechanisms.
Primary Research Targets:
- AMPK Pathway: Research suggests ampk pathway is the primary target of mots c peptide
- Glucose Homeostasis: Experimental data shows effects on glucose utilization and glucose metabolism
- Lipid Metabolism: Findings show effects on fat metabolism and adipose homeostasis
- Insulin Sensitivity: Laboratory studies show effects on insulin resistance mechanisms
The aging process decreases circulating mots c levels, making this compound relevant for research into age related diseases and metabolic dysfunction. Experimental evidence shows mots c plays roles in muscle metabolism and maintaining cellular energy balance during metabolic stress.
Research Studies
Extensive laboratory research has been done on the mitochondrial encoded peptide mots across multiple research areas. Scientists studying metabolic regulation use mots c in receptor-ligand binding studies, enzyme activity assays and cell proliferation experiments to understand its biochemistry.
Current Research Applications:
- Metabolic Studies: Researchers examine glucose homeostasis and systemic metabolism responses
- Cellular Metabolism: Investigations focus on mitochondrial function and energy production pathways
- Bone Research: Studies explore effects on mesenchymal stem cells and promoting osteogenic differentiation
- Cardiovascular Research: Experimental work examines endothelial function and coronary endothelial dysfunction
- Aging Research: Laboratory studies investigate age dependent physical decline and exceptional longevity mechanisms
Research shows mots c promotes various cellular responses through endothelial cells and stem cells interactions. The same study protocols that showed mots c improves osteoporosis related parameters in experimental models are being used in current research. Kim et al and other research groups have shown that findings suggest significant potential for understanding metabolic disorders through this mitochondrial derived peptide.
Experimental protocols often examine how mots c inhibits some pathways while promoting others, especially in diet induced obesity models and ovariectomy induced metabolic dysfunction studies. Cell viability assays and bone marrow studies provide additional research avenues to understand this compound.
Storage and Safety
Proper handling protocols ensure optimal stability and experimental consistency when you buy mots c for your research. The lyophilized peptide requires specific storage conditions to maintain molecular integrity throughout experimental time.
Storage Requirements:
- Long-term Preservation: -20°C recommended for extended stability periods
- Environmental Protection: Shield from bright light and moisture exposure
- Handling Protocol: Allow vials to equilibrate to room temperature before opening
- Reconstituted Solutions: Remain stable for 3+ weeks at +4°C and 3-4 months at -20°C
Laboratory safety protocols require adherence to institutional guidelines for peptide handling. Researchers should implement appropriate personal protective equipment and follow established procedures for working with research compounds. The mots c 10mg vial format provides convenient quantities for most experimental protocols while minimizing waste.
Why Buy from Loti Labs
Loti Labs offers high-purity mots c for demanding research applications with full analytical documentation. Each batch is tested to ensure researchers receive compounds meeting scientific standards.
Quality Assurance:
- Purity Verification: Certificates of analysis show purity above 99%
- Sequence Confirmation: Peptide sequencing verification through advanced analytical methods
- Molecular Weight Validation: Molecular weight confirmation using mass spectrometry
- Packaging Excellence: Glass vial packaging for optimal preservation and stability
- Documentation: Complete analytical profiles with every shipment
Good manufacturing practices (GMP) ensures batch-level consistency for reproducible results. Third-party verification provides additional assurance of compound quality and identity.
Products are for Research Use Only
All products sold by Loti Labs are research chemicals for laboratory use only. This classification is for in-vitro testing, biochemical studies and controlled experimental use. It does not permit human or veterinary use under federal regulations.
Compliance Information:
- Not approved as pharmaceuticals, food additives or cosmetic ingredients
- Not to be misbranded, mislabeled or misused outside of research
- All purchases must comply with federal, state and institutional regulations
- Laboratory use requires safety protocols and trained personnel
Researchers must ensure their research complies with research use only guidelines. Institutional review and approval may be required depending on experimental protocol and research objectives.
Loti Labs Shipping Policy
Loti Labs has a fast shipping process to support your research timeline. Orders placed before 1pm EST Monday-Friday will be processed and shipped the same day. Orders placed after 1pm EST or on weekends will ship the next business day.
Concentrations and Shipping:
- Standard vial sizes: 10mg
- Discreet packaging
- Secure shipping with tracking
The ordering process is designed to fit your research laboratory schedule and ensure proper handling throughout the delivery chain.
30-Day Satisfaction Guarantee
Loti Labs backs research with a 30-day satisfaction guarantee. You can return unopened products for a full refund of the purchase price.
This guarantee reflects our confidence in product quality and manufacturing standards. It allows for changes in research priorities and experimental requirements while keeping your research budget in check.
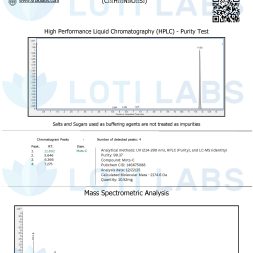
Third Party Testing of Every Batch
Every batch of compounds sold by Loti Labs is tested by a third party. HPLC analysis confirms product purity and identity, while mass spectrometry verifies molecular weight.
Quality Control:
- Independent laboratory verification for each production batch
- HPLC purity analysis with chromatographic profiles
- Mass spectrometry confirmation of molecular identity
- GMP compliance throughout production
- Documentation with every shipment
These tests ensure you receive consistent high quality compounds for demanding research applications. The independent verification process eliminates variability and supports reproducible results.
Summary
The mitochondrial peptide mots c is a research tool to study cellular metabolism, aging and metabolic regulation. Researchers looking to buy mots c need suppliers that verify analytical, document properly and comply with regulations.
Loti Labs meets these requirements with quality assurance programs, third party testing, and research focused customer support. High purity compounds, detailed documentation and fast shipping support productive research across multiple research areas.
For researchers studying metabolic homeostasis, mitochondrial function or age related cellular processes, Loti Labs has the analytical rigor and product consistency for meaningful scientific discoveries. Contact Loti Labs to discuss your research requirements and compound specifications for your next project.
References
- Lee, C., et al. (2015). “MOTS-c: A Mitochondrial-Encoded Peptide that Regulates Metabolic Homeostasis.” Cell Metabolism. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2015.02.009
- Kim, K. H., et al. (2018). “MOTS-c is an Exercise-Induced Mitochondrial-Encoded Regulator of Metabolic Homeostasis.” Cell Metabolism. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2018.04.011
- Lu, J., et al. (2019). “MOTS-c Treatment Prevents Obesity and Insulin Resistance Induced by Ovariectomy in Mice.” Diabetes. https://diabetes.diabetesjournals.org/content/68/2/324
- Reynolds, J. C., et al. (2021). “MOTS-c Enhances Physical Performance and Promotes Healthy Aging in Mice.” Aging Cell. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.13399
- US Anti-Doping Agency (USADA). “What is MOTS-c Peptide?” https://www.usada.org/spirit-of-sport/what-is-mots-c-peptide
- Peptides.org. “MOTS-c Reviews, Clinical Studies, and Safety.” https://www.peptides.org/mots-c
- ProSpec Bio. “MOTS-C Peptide | MOTS-C Synthetic Hormone.” https://www.prospecbio.com/mots-c
| Weight | .03125 lbs |
|---|