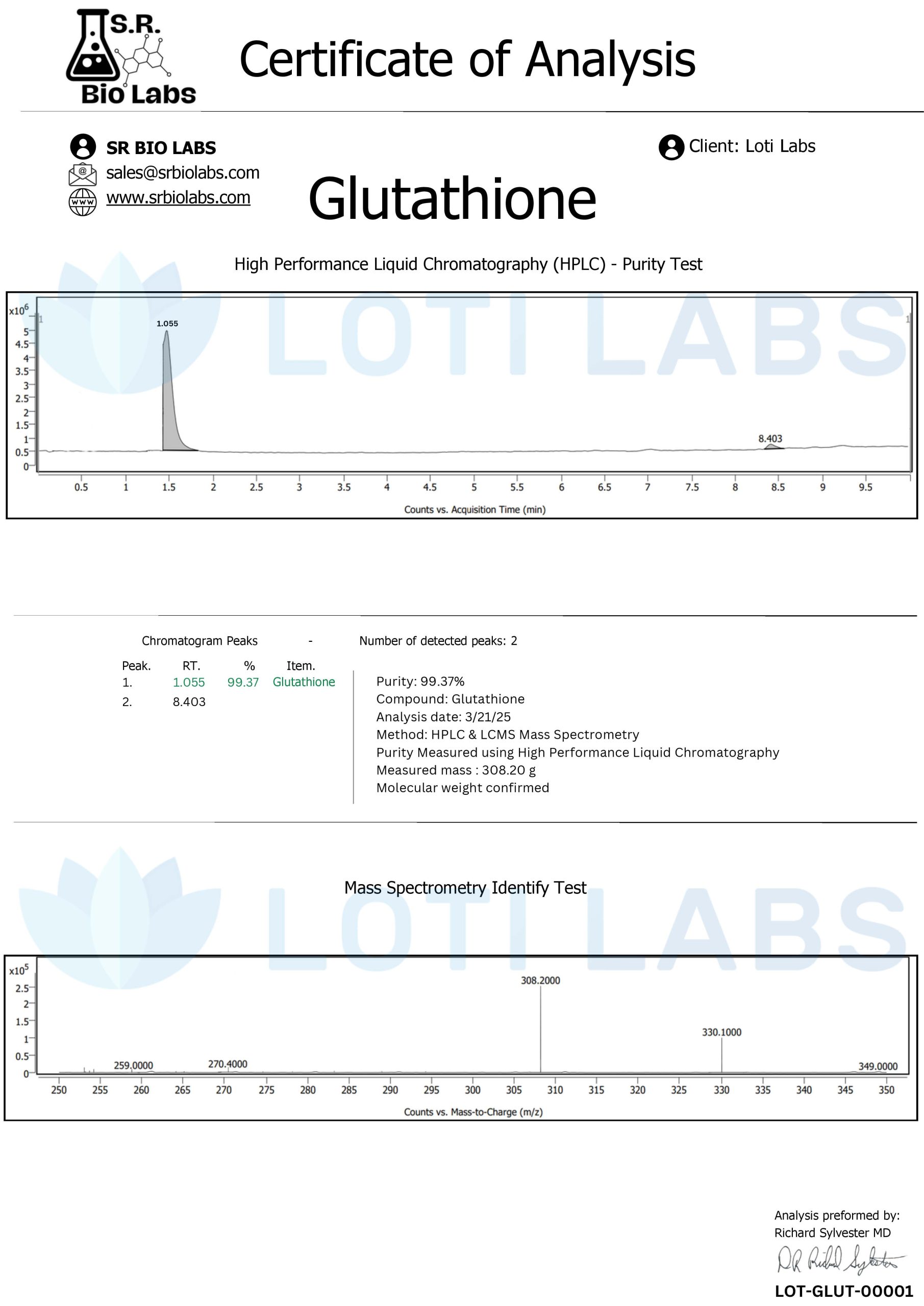
Glutathione 600mg
$79.99
You save

Glutathione For Sale at Loti Labs
When examining glutathione in research contexts, it’s important to consider what laboratory studies suggest about this compound. This research overview will explore the observed properties, laboratory safety assessments, and experimental efficacy based on current scientific literature. Let’s examine what makes glutathione a substance of interest in research settings and the findings that make it noteworthy.
Key Takeaways
- Research indicates glutathione functions as a significant antioxidant compound that may reduce oxidative stress in experimental models, enhance detoxification processes in laboratory settings, and support immune function in research specimens.
- Laboratory investigations with glutathione or its precursors suggest potential biochemical activities, though these observations require further rigorous scientific validation through controlled studies.
- Current scientific literature on glutathione predominantly consists of animal-model investigations, highlighting the critical need for more comprehensive laboratory trials to accurately assess its properties in various research contexts.
Understanding Glutathione
In research settings, glutathione presents as a tripeptide compound. It comprises three amino acids: cysteine, glycine, and glutamine. This specific molecular structure appears to contribute to its antioxidant properties observed in laboratory conditions. But what exactly do research models demonstrate about glutathione’s biochemical activities? Scientific investigations suggest that glutathione plays roles in reducing oxidative stress, facilitating detoxification processes, and modulating immune responses in experimental systems.
Oxidative stress represents a biochemical state characterized by imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in biological specimens. Research suggests this imbalance can lead to cellular alterations in experimental models. Laboratory studies indicate that glutathione, through its antioxidant properties, may help neutralize these free radicals in test environments, potentially reducing oxidative stress markers and protecting cellular structures in research specimens.
Detoxification represents another area of interest in glutathione research. Studies suggest it participates in the biotransformation and elimination of various substances from biological systems, particularly in liver models. Research indicates that glutathione appears vital for hepatic detoxification pathways and might offer protective effects in liver-damage models. Supporting these metabolic pathways, research suggests glutathione enhances overall cellular health in laboratory specimens.
In experimental settings, glutathione can be administered through various methods, including direct administration, topical application, and oral introduction in research models. Each method presents distinct experimental considerations, with direct administration offering the most immediate bioavailability in research specimens. It’s essential to note that the products available from Loti Labs are strictly for research purposes only, not intended for any other use, including compounds like liposomal glutathione and toniiq glutathione.
Research Observations of Glutathione Peptide
Laboratory investigations suggest glutathione may influence various biological parameters through multiple mechanisms. Research models indicate that glutathione might affect cellular responses associated with certain conditions and alter biochemical markers in experimental settings. This research potential has positioned glutathione as a compound of significant interest in the scientific community.
Experimental observations have documented changes in tissue conditions and biological parameters following glutathione administration in research models. These laboratory findings, while preliminary, offer valuable insights into potential research applications. Controlled studies frequently report observable alterations in tissue appearance, cellular markers, and metabolic parameters in experimental specimens exposed to glutathione compounds.
Moreover, research suggests that glutathione is consistently associated with certain biochemical outcomes in laboratory settings. Experimental models exhibit altered energy utilization and metabolic function as research endpoints following glutathione administration. These observations, while promising for further investigation, are based on controlled laboratory conditions and require additional validation through rigorous scientific protocols.
The compounds available through Loti Labs are exclusively intended for research applications. The observations discussed here derive primarily from animal-model studies and should be interpreted within appropriate scientific context. As we explore the antioxidant properties, immune system interactions, and hepatic support functions of glutathione in research settings, it’s important to recognize that these findings represent experimental observations rather than definitive conclusions.
Antioxidant Properties
Glutathione functions as a vital antioxidant compound in cellular environments, potentially helping to mitigate oxidative stress according to laboratory findings. Research suggests this substance may effectively neutralize free radicals, positioning glutathione as a noteworthy component in antioxidant defense mechanisms. Laboratory investigations indicate that glutathione administration could influence markers of oxidative stress and immune responses, highlighting interesting research possibilities for overall physiological function.
Animal-based experimental models have demonstrated that glutathione administration might influence various physiological responses, including antioxidant activity and pigmentation changes in dermal tissues. These research findings point to glutathione potentially playing a role in maintaining dermal tissue integrity and reducing oxidative damage in controlled settings. However, it’s critically important to recognize these observations derive exclusively from animal models and should not be extrapolated beyond the research context without comprehensive further investigation.
The reduced form of glutathione appears to demonstrate optimal bioavailability and potent antioxidant capabilities in laboratory settings. This particular molecular configuration seems crucial for maintaining experimental antioxidant defense systems and achieving measurable reduction in oxidative stress markers. Research suggests that by supporting the reduction of oxidative parameters, glutathione helps protect cellular structures from experimental damage, contributing to interesting research opportunities in physiological maintenance.
It’s essential to note that the compounds provided by Loti Labs are strictly for research purposes and not intended for human use. The research observations discussed here stem from animal studies, and additional investigation is necessary to fully comprehend the extent of glutathione’s antioxidant properties in various experimental models.
Immune System Function
Glutathione appears to play a significant role in modulating immune responses in research settings, potentially helping experimental models respond to various challenges. Research suggests that glutathione’s function in immune system mechanics is noteworthy, as it appears to help regulate responses to experimental stressors. Animal studies indicate that glutathione might enhance defense mechanisms against introduced pathogens and reduce inflammatory markers associated with various experimental conditions. By potentially modulating immune responses, glutathione contributes to interesting research avenues in immune function. These findings highlight research possibilities, though further controlled studies are needed to confirm these experimental observations.
One of the mechanisms through which glutathione supports immune function in research models involves maintaining balance between oxidative markers and inflammatory responses. By potentially reducing oxidative parameters, glutathione may help prevent excessive inflammatory reactions, which can be detrimental in experimental settings. This balance appears crucial for maintaining optimal function in research models and preventing chronic alterations in physiological states.
The compounds offered by Loti Labs are exclusively for research purposes and not intended for human use. The research observations discussed here derive from animal studies, and additional investigation is necessary to fully understand glutathione’s role in immune function across different experimental contexts.
Liver Support
Glutathione appears essential for detoxification processes in liver tissue, potentially aiding in the elimination of harmful substances in research models. Laboratory findings indicate that glutathione is integral for liver detoxification pathways and might help protect against experimental liver damage. This detoxification role seems crucial for maintaining liver function and metabolic processes in research settings.
Research suggests that glutathione administration can improve liver parameters and reduce cellular alterations in experimental models of fatty liver conditions. By potentially supporting the liver’s ability to neutralize harmful compounds, glutathione helps prevent tissue alterations and promotes metabolic stability in laboratory settings. These findings highlight interesting research directions regarding glutathione in liver support and detoxification processes.
Laboratory investigations indicate that glutathione might aid in preventing liver damage and improving metabolic parameters in experimental models of fatty liver conditions. These studies suggest that glutathione’s role in liver health merits further investigation, though additional research is needed to confirm these effects across different experimental models. The liver’s detoxification capacity and metabolic function appear crucial in research exploring physiological maintenance.
The compounds provided by Loti Labs are strictly for research purposes and not intended for human use. The research observations discussed here derive from animal studies, and additional investigation is necessary to fully understand glutathione’s role in liver support across varied experimental contexts.
Glutathione Precursors
Glutathione precursors, like N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and cysteine, serve as critical building blocks that research indicates may support the body’s natural glutathione production processes. These fascinating compounds provide the necessary components for glutathione synthesis in laboratory settings, highlighting their potential significance in experimental models focused on maintaining optimal glutathione levels.
Research suggests that certain nutrients such as vitamins C and E, alongside protein sources, may play interesting roles in supporting glutathione levels in research models. These nutrients appear to contribute to antioxidant defense mechanisms in experimental settings. Studies indicate that elevated glutathione levels might be associated with reduced oxidative stress in various chronic conditions observed in research specimens, underscoring the scientific interest in these precursors.
Interesting findings show that compounds like rosemary extract have demonstrated significant increases in glutathione levels in laboratory settings. This suggests that certain botanical compounds might enhance glutathione synthesis in research models. These observations point to potential avenues for exploring dietary and supplemental strategies in controlled research environments.
The compounds offered by Loti Labs are strictly for research purposes only. The scientific observations discussed here derive exclusively from animal studies, and additional research is necessary to fully elucidate the role of glutathione precursors in various biological systems.
N-Acetylcysteine (NAC)
N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) functions as a key precursor in glutathione synthesis within research models, where glutathione appears to support various biological functions. In laboratory settings, NAC has been observed to contribute to glutathione levels by providing cysteine, one of three amino acids necessary for glutathione formation.
Research indicates that glycine, cysteine, and glutamic acid collectively form the tripeptide structure of glutathione. These amino acids are typically derived from protein sources in experimental models, highlighting the potential importance of protein availability in research settings examining glutathione synthesis. Interestingly, studies suggest that protein processing efficiency may influence glutathione production capacity in research specimens.
The administration of NAC in controlled research environments represents one approach to studying glutathione level modulation. By providing necessary precursors, researchers can observe how NAC might support antioxidant defense systems in various experimental models. It’s important to clarify that the compounds provided by Loti Labs are exclusively intended for research applications.
These scientific observations stem from animal studies conducted in controlled laboratory environments, and continued research is needed to expand our understanding of NAC’s role in glutathione synthesis pathways and broader biochemical functions.
Research and Clinical Studies
Research and scientific investigations play vital roles in expanding our knowledge about glutathione’s functions and potential effects. These studies help scientists develop a clearer picture of how glutathione operates within various biological systems. The literature reviewed included investigations focusing on glutathione’s potential skin-lightening properties in controlled settings, encompassing various study designs such as randomized controlled trials and observational analyses. However, researchers emphasize that careful consideration of causality relationships and genetic factors remains essential for proper scientific interpretation.
Comprehensive and methodically designed investigations are necessary to address existing knowledge gaps in glutathione research. Such studies would potentially provide more concrete insights into this fascinating compound. Future research might benefit from focusing on safety profiles, efficacy parameters, and potential biological responses across diverse experimental models. The selection criteria for studies in this field typically emphasize safety considerations and relevance to dermatological research questions.
The compounds available through Loti Labs are strictly intended for research applications only. The scientific observations discussed here come from animal studies conducted in controlled settings, and additional investigation is required to enhance our understanding of glutathione’s biochemical properties and functions.
Animal Studies
Animal-based research has yielded fascinating insights into glutathione’s potential properties and effects. Research suggests that glutathione may play roles in immune response modulation and reduction of inflammatory markers associated with certain autoimmune conditions in research models. These studies highlight interesting avenues for exploring glutathione’s potential in supporting immune function research and investigating chronic condition mechanisms.
For example, laboratory investigations indicate that glutathione appears to interact with immune response pathways, potentially influencing inflammatory processes associated with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis in animal models. Through these regulatory mechanisms, glutathione might affect how biological systems respond to immune challenges and manage inflammatory processes in experimental settings.
Research suggests that modulating glutathione levels in laboratory specimens might influence the expression of symptoms associated with certain chronic conditions, including autoimmune manifestations. These findings point to intriguing research directions regarding glutathione’s role in maintaining biological equilibrium. However, it’s crucial to approach these results with appropriate scientific caution, recognizing they derive from controlled animal studies rather than definitive conclusions.
The compounds provided by Loti Labs are exclusively for research purposes. The scientific observations presented here come from animal studies conducted under controlled conditions, and further
Summary
In summary, glutathione is a fascinating tripeptide composed of cysteine, glycine, and glutamine, which laboratory investigations reveal plays a crucial role in reducing oxidative stress, enhancing detoxification processes, and modulating immune system functionality. Research suggests that glutathione administration, through various experimental methods such as intravenous delivery, topical application, and oral formulations, may demonstrate promising outcomes in research settings.
Animal studies indicate that glutathione exhibits significant antioxidant properties, supporting immune system function and hepatic health in laboratory models. These investigations suggest that glutathione may shield cells from damage, enhance immune responses, and facilitate hepatic detoxification processes. However, it’s critical to emphasize that these findings stem exclusively from animal models and should not be extrapolated beyond the research context without further rigorous investigation.
Glutathione precursors, such as N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and cysteine, demonstrate vital roles in supporting glutathione synthesis in experimental settings. By providing the necessary building blocks, research suggests these precursors help maintain optimal glutathione levels in laboratory specimens, contributing to the cellular mechanisms being studied.
The research and laboratory investigations discussed highlight potential applications of glutathione in experimental contexts. However, it remains imperative to conduct further research, particularly well-designed controlled trials, to fully comprehend the mechanisms and effects of this compound. The substances discussed are intended exclusively for research purposes, and the observations mentioned derive solely from animal studies conducted in controlled laboratory environments.
In conclusion, glutathione presents intriguing possibilities as a vital molecule for biochemical research. As scientific investigation continues to unfold, the potential applications of glutathione in supporting antioxidant defense mechanisms, immune system function, and hepatic health in experimental models becomes increasingly evident. Let this exploration inspire further scientific inquiry into the potential of glutathione in research settings, always maintaining commitment to rigorous scientific methodology and evidence-based conclusions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role does glutathione play in Research?
Glutathione demonstrates a crucial role in reducing oxidative stress, enhancing detoxification processes, and regulating immune system function in research models, making it an essential compound for laboratory investigation. Research suggests its antioxidant properties help protect cellular structures from damage and support natural defense mechanisms in experimental settings.
How can glutathione administration be achieved in research contexts?
Glutathione can be administered through intravenous delivery, topical application, or oral formulations in laboratory settings, each offering different experimental outcomes and absorption patterns. Research suggests selecting an appropriate administration method aligned with specific research questions and experimental design is fundamental for generating reliable data.
What are some potential benefits of glutathione based on animal studies?
Research suggests that glutathione may provide notable antioxidant effects, enhance immune system functionality, and assist in hepatic detoxification in animal models. These observed outcomes in laboratory settings underscore its potential significance in biochemical research and warrant further investigation.
What are glutathione precursors, and why are they important in research?
Glutathione precursors, like N-acetylcysteine and cysteine, are fundamental compounds for investigating glutathione synthesis in laboratory settings. Research suggests ensuring adequate levels of these precursors supports optimal glutathione production in experimental models, which appears essential for cellular function and detoxification processes being studied.
Why is further research needed for glutathione investigations?
Further research is essential to comprehensively understand the mechanisms and effects of glutathione in experimental settings, as current observations primarily derive from animal studies rather than comprehensive controlled trials. This knowledge gap underscores the necessity for more rigorous investigation to validate the properties and applications of this compound in research contexts, ensuring findings are based on sound scientific evidence rather than preliminary observations.
References
- Pizzorno, J. (2014). Glutathione! Integrative Medicine: A Clinician’s Journal, 13(1), 8-12.
- Richie, J. P., et al. (2015). Randomized controlled trial of oral glutathione supplementation on body stores of glutathione. European Journal of Nutrition, 54(2), 251-263.
- Wu, G., et al. (2004). Glutathione metabolism and its implications for health. The Journal of Nutrition, 134(3), 489-492.
- Allen, J., et al. (2011). Glutathione and its role in the immune system. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 128(4), 747-759.
- Witschi, A., et al. (1992). The systemic availability of oral glutathione. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 43(6), 667-669.
- Lu, S. C. (2013). Glutathione synthesis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) – General Subjects, 1830(5), 3143-3153.
- Ballatori, N., et al. (2009). Glutathione dysregulation and the etiology and progression of human diseases. Biological Chemistry, 390(3), 191-214.
- Franco, R., et al. (2007). Glutathione Efflux and Cell Death. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 9(9), 1327-1349.
- Townsend, D. M., et al. (2003). The importance of glutathione in human disease. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 57(3-4), 145-155.
- Meister, A., & Anderson, M. E. (1983). Glutathione. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 52(1), 711-760.
These references provide a comprehensive overview of the role of glutathione in health, its metabolism, and its potential benefits and mechanisms as discussed in the article.
| Weight | 0.15 lbs |
|---|
 Selank 10mg
Selank 10mg